Asus P4G8X P4G8X User Manual - Page 129
Creating RAID Sets, Deleting RAID Sets, Resolving Conflicts
 |
View all Asus P4G8X manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 129 highlights
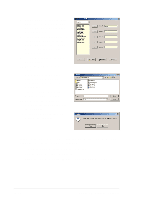
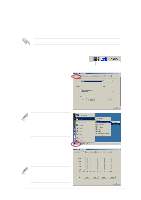
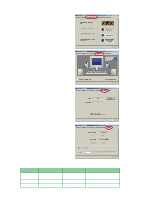
Creating RAID Sets 1. Select the option Create RAID Set. 2. Choose either a Striped or Mirrored RAID Set. 3. You may choose to auto-configure or manually configure the RAID Set. For Striped Sets, you can change the chunk size. For Mirrored Sets, you can specify the Source and Target drives, and create a Disk Copy. What is a chunk? The chunk size is the "stripe" on each disk. It is the unit of storage equivalent to one stripe on a RAID 0 set. Available chunk sizes: [2] [4] [8] [16] [32] [64] [128] When manually setting the chunk size for your RAID set, it is recommended to use the smaller chunk size for server applications and the larger chunk size for AV applications. What is Disk Copy? If the disk assigned as the Source drive has been previously partitioned and has data stored in it, and a second drive is added, the data on the source drive can be copied to the Target drive. This makes the Source and the Target drives identical. All subsequent data will be written to both drives as a Mirrored set. However, if the Source drive does not have data stored in it, there is no need for Disk Copy. 4. When the utility prompts you with "Are You Sure? (Y/N)" before completing the configuration, press "Y" to confirm or "N" to return to the configuration options. Deleting RAID Sets 1. To remove one or more RAID sets, select the option Delete RAID Set. 2. Select the RAID set to delete, and press "Y" when asked "Are You Sure? (Y/N)." Resolving Conflicts When a RAID set is created, the metadata written to the disk includes drive connection information (Primary Chanel, Secondary Chanel). If, after a disk failure, the replacement disk was previously part of a RAID set (or used in another system), it may have conflicting metadata, specifically in the drive connection information. If so, this will a RAID set can neither be created nor rebuilt. In order for the RAID set to function properly, this old metadata must be first overwritten with the new metadata. To resolve this, select the option Resolve Conflict so that the correct metadata (including the correct drive connection information) may be written to the replacement disk. ASUS P4G8X series motherboard user guide 5-25