Belkin F5D7632uk4 F5D7632uk4 User Manual - English - Page 37
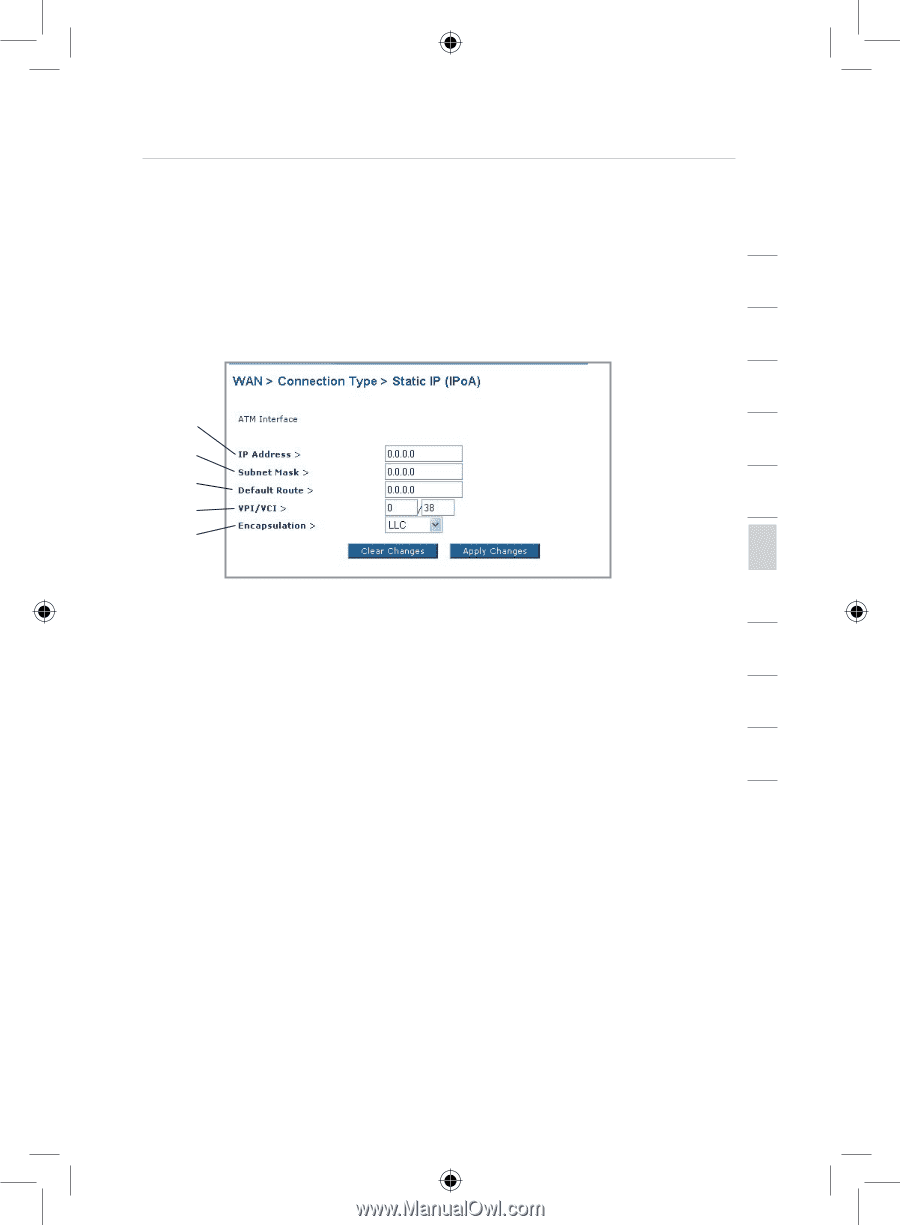
Setting your ISP Connection to Static IP IPoA, IP Address, Subnet Mask, Default Route, VPI/VCI,
 |
View all Belkin F5D7632uk4 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 37 highlights
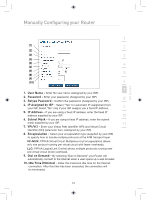
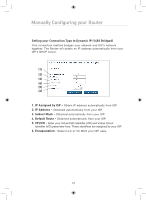
Manually Configuring your Router 1 Setting your ISP Connection to Static IP (IPoA) This connection type is also called "Classical IP over ATM" or "CLIP", which your ISP provides a fixed IP for your Router to connect to 2 the Internet. 3 4 (1) (2) 5 (3) 6 (4) (5) 7 8 1. IP Address - Enter an IP address assigned by your ISP for the Router WAN interface. 9 2. Subnet Mask - Enter a subnet mask assigned by your ISP. 3. Default Route - Enter a default gateway IP address. If the Router cannot find the destination address within its local network, it will 10 forward the packets to the default gateway assigned by your ISP. 4. VPI/VCI - Enter your Virtual Path Identifier (VPI) and Virtual Circuit 11 Identifier (VCI) parameter here. These identifiers are assigned by your ISP. 12 5. Encapsulation - Select LLC or VC MUX your ISP uses. section 35