Belkin F5D8236-4 User Manual - Page 37
Changing the Wireless Channel, Extension Channel, Using the Wireless Mode Switch - 802 11 n wireless router
 |
UPC - 722868680636
View all Belkin F5D8236-4 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 37 highlights
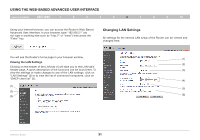
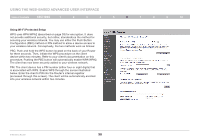
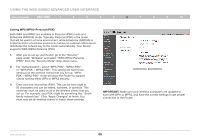
Using the Web-Based Advanced User Interface Table of Contents sections 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Changing the Wireless Channel There are a number of operating channels from which you can choose- in the United States, there are 11 and in the United Kingdom (and most of Europe), there are 13. In a small number of other countries, there are other channel requirements. Your Router is configured to operate on the proper channels for the country in which you reside. The channel can be changed if needed. If there are other wireless networks operating in your area, your network should be set to operate on a channel that is different than the other wireless networks. Extension Channel The IEEE 802.11n draft specification allows the use of a secondary channel to double the bandwidth (see "Using the Bandwidth Switch" below). An appropriate extension channel will be displayed when operating in 40MHz mode (see "Using the Wireless Mode Switch" below). The channel can be changed if needed. Using the Wireless Mode Switch This switch allows you to set the Router's wireless modes. There are several modes. 1) Off This mode will turn OFF the Router's access point, so no wireless devices can join the network. Turning off the wireless function of your Router is a great way to secure your network when you are away from home for a long period of time, or don't want to use the wireless feature of the Router at a certain time. 2) 802.11g only Setting the Router to this mode will allow only 802.11g-compliant devices to join the network, keeping out any slower 802.11b devices. 3) 802.11b+g+n Setting the Router to this mode will allow 802.11b-, 802.11g-, and 802.11n-compliant devices to join the network. 4) 802.11n only Setting the Router to this mode will allow only N/draft 802.11n-compliant devices to join the network, keeping out 802.11g and 802.11b devices. Note: Some modes may require firmware updates to be enabled. N Wireless Router 35