Cisco ASR1002 Configuration Guide - Page 366
Creating or Deleting a Bridge Domain Interface, Bridge Domain Interface Scalability, How - esp5
 |
UPC - 882658196416
View all Cisco ASR1002 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 366 highlights
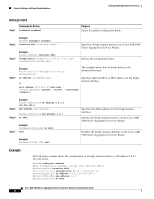
Creating or Deleting a Bridge Domain Interface Configuring Bridge Domain Interfaces When packets flow from a Layer 2 bridge domain network to a Layer 3 routing network through the bridge domain interface, the packets are treated as bridge domain interface input packets and bytes. When packets arrive at a Layer 3 interface and are forwarded through the bridge domain interface to a Layer 2 bridge domain, the packets are treated as output packets and bytes, and the counters are updated accordingly. A BDI maintains a standard set of Layer 3 packet counters as the case with all Cisco IOS interfaces. Use the show interface command to view the Layer 3 packet counters. The convention of the counters is relative to the Layer 3 cloud, for example, input refers to the traffic entering the Layer 3 cloud from the Layer 2 BD, while output refers to the traffic leaving the Layer 3 cloud to the Layer 2 BD. Use the show interfaces accounting command to display the statistics for the BDI status. Use the show interface command to display the overall count of the packets and bytes that are transmitted and received. Creating or Deleting a Bridge Domain Interface When you define an interface or subinterface for a Cisco IOS router, you name it and specify how it is assigned an IP address.You can create a bridge domain interface before adding a bridge domain to the system, this new bridge domain interface will be activated after the associated bridge domain is configured. Note When a bridge domain interface is created, a bridge domain is automatically created. When both bridge domain interface and bridge domain are created, the system maintains the required associations for mapping the bridge domain-bridge domain interface pair. The mapping of bridge domain and bridge domain interface is maintained in the system. The bridge domain interface uses the index of the associated bridge domain to show the association. Bridge Domain Interface Scalability Table 6 lists the bridge domain interface scalability numbers, based on the type of Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Router's Forwarding Processors. Table 6 Bridge Domain Interface Scalability Numbers Based on the Type of Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Router's Forwarding Processors Description Maximum bridge domain interfaces per router ASR1000-ESP5, ASR1000-ESP10, ASR 1001, ASR1000-ESP10-N, ASR 1002-F (ESP2.5) ASR1000-ESP20 ASR1000-ESP40 4096 4096 4096 How to Configure a Bridge Domain Interface To configure a bridge domain interface, perform the following steps: Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers Software Configuration Guide 6