Cisco WAP200 Administration Guide - Page 62
VLAN support - set dhcp
 |
UPC - 745883574452
View all Cisco WAP200 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 62 highlights
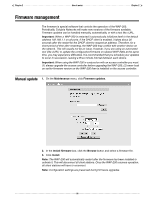
Chapter 2 How it works Chapter 2 VLAN support The WAP-200 provides a robust and flexible VLAN (802.1q) implementation. VLANs can be defined on the LAN ports, as well as on wireless links. User traffic can be mapped to a VLAN on a per-VSC basis, or on a per-user basis. For scenarios that illustrate how to work with VLANs, see the Colubris Networks Configuration Guide. Creating VLANs Use the following steps to create a VLAN: 1. Open the Network > Ports page. Under VLAN configuration you can view a list of all defined VLANs. Initially this list is empty. 2. Click Add New VLAN. This opens the Add/Edit VLAN page, where you define the characteristics of the VLAN. Define settings as follows: General • Port-Select the port that the VLAN is associated with. • VLAN ID-Specify an ID for the VLAN (802.1q). The same VLAN ID can be assigned to different ports to create a VLAN bridge across the ports. If the VLAN is being assigned to an Ethernet port you can also define a range of VLANs in the form X-Y. Where X and Y can be 1 to 1024. For example: 50-60 Note: An IP address cannot be assigned when you define a range of VLANs. • VLAN name-Specify a name for the VLAN. This name is used to identify the VLAN on the WAP-200 and has no operational significance. Assign IP address via An IP address cannot be assigned when the VLAN ID is defined as a range. • DHCP client-The VLAN obtains its IP address from a DHCP server on the same VLAN. • Static-Assign a static IP address and mask. • None-No IP address is assigned. 62