D-Link DAP-2660 User Manual - Page 19
Wireless Security, Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
 |
View all D-Link DAP-2660 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 19 highlights
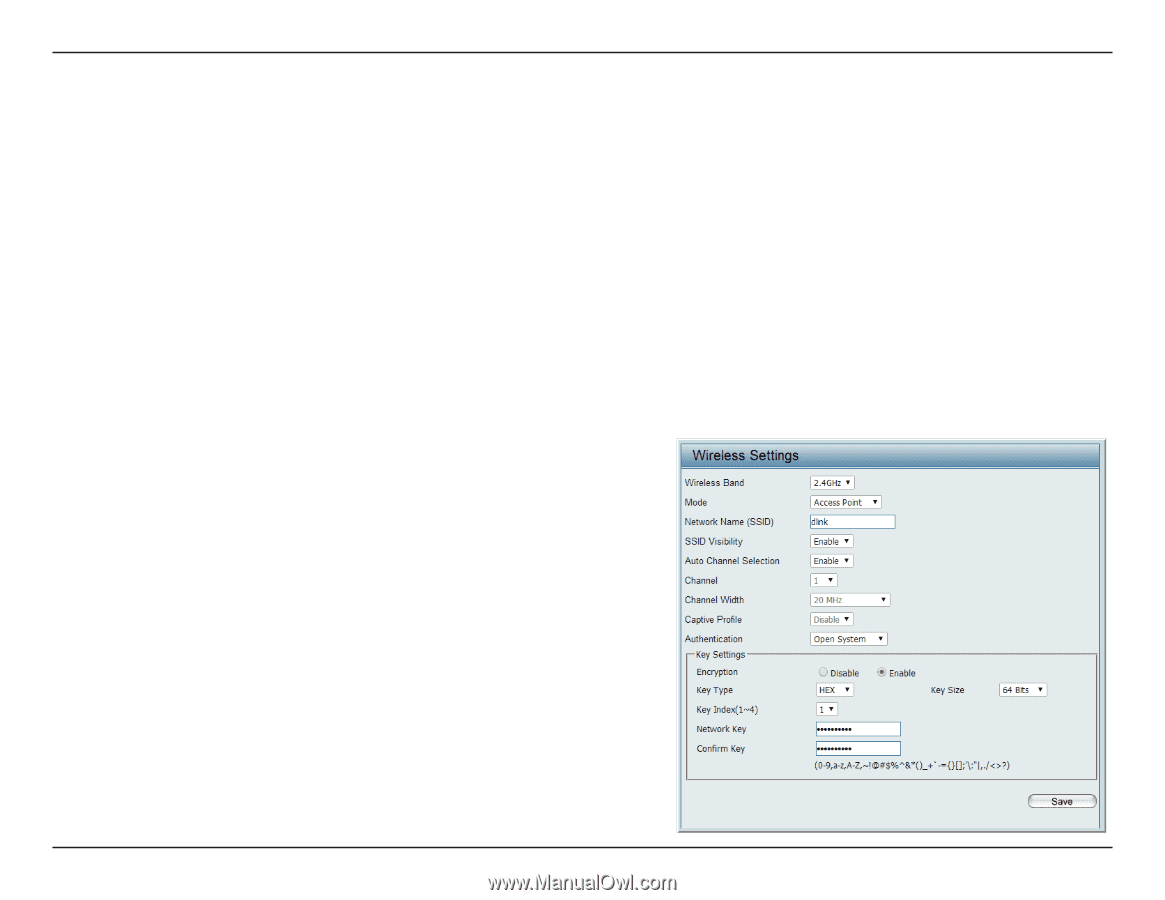
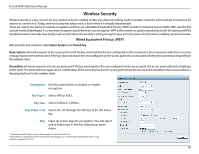
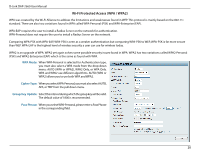
D-Link DAP-2660 User Manual Wireless Security Wireless security is a key concern for any wireless network installed. Unlike any other networking method wireless networks will broadcast it's presence for anyone to connect to it. Today, wireless security has advanced to a level where it is virtually impenetrable. There are mainly two forms of wireless encryption and they are called Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA). WEP was the first security method developed. It is a low level encryption but better than now encryption. WPA is the newest encryption standard and with the advanced WPA2 standard wireless networks have finally reach a point where the security is strong enough to give users the peace of mind when installing wireless networks. Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) WEP provides two variations called Open System and Shared Key. Open System will send a request to the access point and if the key used matches the one configured on the access point, the access point will return a success message back to the wireless client. If the key does not match the one configured on the access point, the access point will deny the connection request from the wireless client. Shared Key will send a request to the access point and if the key used matches the one configured on the access point, the access point will send a challenge to the client. The client will then again send a confirmation of the same key back to the access point where the access point will either return a successful or a denial packet back to the wireless client. Encryption: Use the radio button to disable or enable encryption. Key Type*: Select HEX or ASCII. Key Size: Select 64 Bits or 128 Bits. Key Index (1-4): Select the 1st through the 4th key to be the active key. Key: Input up to four keys for encryption. You will select one of these keys in the Key Index drop-down menu. **Hexadecimal (HEX) digits consist of the numbers 0-9 and the letters A-F. *ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) is a code that represents English letters using numbers ranging from 0-127. 19