Dell EqualLogic PS6210XS EqualLogic PS Series Storage Arrays iSCSI Initiator a - Page 9
General Network Requirements
 |
View all Dell EqualLogic PS6210XS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 9 highlights
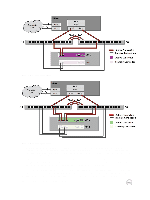
3 Configure Your Network for High Availability A Dell EqualLogic iSCSI SAN can be operated in any network that supports the industry standards and IP subnet design guidelines described in this section. Because of this flexibility, many network design and configuration choices can affect SAN performance. For additional network design and configuration information to support the use of a Dell EqualLogic SAN, see the PS Series Configuration Guide. This guide can be downloaded from: http://en.community.dell.com/techcenter/storage/w/wiki/equallogic-configuration-guide General Network Requirements This section outlines the general best practices for configuring a redundant iSCSI network. Design Network for Redundancy For Dell EqualLogic PS Series arrays, follow these general SAN design requirements. Ports • Dell recommends that, whenever possible, the arrays should be in the same subnet as the group's IP address. For all members (arrays) in a given SAN group, all array Ethernet ports should be connected to the same subnet. This connection allows the arrays to communicate with each other as a group of peer members. • At least two iSCSI SAN ports per host must be connected to two different switches in a SAN fabric for fully redundant SAN connectivity. Switches • All switches within the SAN must be interconnected such that a path is always present from any Ethernet port on one array to all other Ethernet ports on all other arrays in the group. The preferred method of interconnect is stacking the switches. • Enabling jumbo frames on all switches in the SAN is a recommended best practice as long as the rest of the infrastructure (such as initiators and NICs) supports jumbo frames as well. This requirement applies to SANs connected to either a PS Series array or an FS Series appliance. • Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol must be enabled if the SAN infrastructure has more than two switches in a nonstacked configuration, and portfast must be enabled on all edge device ports (hosts, and FS Series appliances and PS Series arrays). • To prevent a switch failure from also disabling all paths between a host and its connected volumes, all ports from each controller must be connected to at least two different switches. This requirement also applies to FS Series NAS appliance configurations. For PS4100/PS6100 family arrays, split the vertical port pair connections between two switches to ensure that 100percent bandwidth capability is maintained in the event of a vertical port failover. Split the connections as shown in Figure 1. Redundant SAN PS4100 and Figure 2. Redundant SAN PS6100. Configure Your Network for High Availability 9