Dell EqualLogic PS6210XV EqualLogic Multipathing Extension Module Installation - Page 8
Related Documentation
 |
View all Dell EqualLogic PS6210XV manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
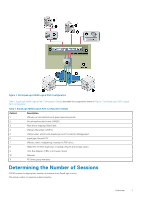
1. Calculating the optimal number of sessions to maximize the bandwidth between the host and the member. This calculation takes into account the speed of available host adapters and network interface cards (NICs) on each member hosting part of the volume. The algorithm does not create unnecessary sessions when no performance benefit results. Therefore, in configurations with limited numbers of computer and member Ethernet ports, the actual number of sessions created might be fewer than the user limits specified in step 2. Example A: You have 2 x 1 Gb host NICs, and are connecting to a volume on members with 4 x 1 Gb eth ports. The optimal number of sessions is 2 per member, because that will saturate the host NICs. Example B: You have 1 x 10 Gb host NICs, and are connecting to a volume on members with 4 x 1 Gb eth ports. The optimal number of sessions is 4 per member, because that amount will saturate the member eth ports. Example C: You have 2 x 10 Gb host NICs, and are connecting to a volume on members with 1 x 10 Gb eth ports. The optional number of sessions is 1 per member, because that amount will saturate the member eth ports. 2. Applying any user-configured session limits. The default behavior is to limit to 2 sessions per volume slice or 6 sessions per volume, whichever is reached first. However, you can modify these limits, as described in EHCM Configuration File. 3. Applying a per-pool throttle to ensure the group remains below 90 percent of the maximum number of allowed connections per pool. This throttling logic ensures the connections are equitably shared among all the pool members and all the hosts using HIT multipathing to connect to volumes on the group. See the Dell EqualLogic PS Series Storage Array Release Notes for the current configuration limits. The number of sessions created by EHCM depends on the topology of your iSCSI SAN and the MPIO settings on the VMware ESXi host. Every volume is distributed across one or more members in the PS Series group. The portion of a volume that is located on a single member is referred to as a volume slice. The default EHCM behavior is to create two sessions per volume slice, with a maximum of six sessions per volume. However, you can alter this behavior (see EHCM Configuration File). When you use the Dell EqualLogic MEM, EHCM distributes iSCSI sessions across all configured VMkernel ports and PS Series group Ethernet ports. EHCM monitors the topology of the SAN. If you change the configuration by modifying the number of Ethernet interfaces, or by moving a PS Series volume, or if a network outage affects some of the iSCSI sessions, EHCM automatically reconfigures the iSCSI sessions to reflect these changes. Related Documentation It is beyond the scope of this document to provide VMware conceptual information or detailed instructions on configuring VMware vSphere. See the following related documentation. VMware Documentation See the VMware documentation website. Specifically, refer to the following documents: • vSphere Installation and Setup Guide • iSCSI SAN Configuration Guide • Installing and Administering vSphere Update Manager Dell EqualLogic Product Documentation For details about managing VMware virtual volumes (VVols), see the following Dell EqualLogic documents: • Dell Virtual Storage Manager for VMware Installation and User's Guide • Dell EqualLogic Group Manager Administrator's Guide Dell EqualLogic Tech Report For information about the benefits of the Dell EqualLogic MEM, see the Dell EqualLogic Configuring and Installing the PS Series Multipathing Extension Module for VMware vSphere and PS Series. Dell EMC PowerStore Documentation For details about importing EqualLogic storage to a PowerStore array, see Importing External Storage to PowerStore Guide. 8 Overview