Dell OptiPlex GX260N User Guide - Page 28
Hyper-Threading, Hung Computer
 |
View all Dell OptiPlex GX260N manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 28 highlights
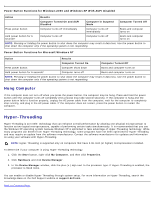
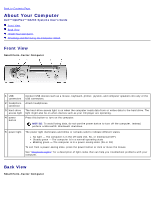
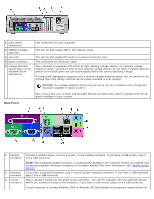
Power Button Functions for Windows 2000 and Windows XP With ACPI Disabled Action Results Computer Turned On and ACPI Disabled Computer in Suspend Mode Computer Turned Off Press power button Computer turns off immediately Computer turns off immediately Boots and computer turns on Hold power button for 6 seconds* Computer turns off Computer turns off Boots and computer turns on NOTE: Pressing or holding the power button to shut down the computer may result in data loss. Use the power button to shut down the computer only if the operating system is not responding. Power Button Functions for Microsoft Windows NT Action Results Computer Turned On Computer Turned Off Press power button Computer shuts down Boots and computer turns on Hold power button for 6 seconds* Computer turns off Boots and computer turns on NOTE: Pressing or holding the power button to shut down the computer may result in data loss. Use the power button to shut down the computer only if the operating system is not responding. Hung Computer If the computer does not turn off when you press the power button, the computer may be hung. Press and hold the power button until the computer turns off completely (this process may take several seconds). If the computer is hung and the power button fails to function properly, unplug the AC power cable from the computer, wait for the computer to completely stop running, and plug in the AC power cable. If the computer does not restart, press the power button to restart the computer. Hyper-Threading Hyper-Threading is an Intel® technology that can enhance overall performance by allowing one physical microprocessor to function as two logical microprocessors, capable of performing certain tasks simultaneously. It is recommended that you use the Windows XP operating system because Windows XP is optimized to take advantage of Hyper-Threading technology. While many programs can benefit from Hyper-Threading technology, some programs have not been optimized for Hyper-Threading and may require an update from the software manufacturer. Contact the software manufacturer for updates and information on using your software with Hyper-Threading. NOTE: Hyper-Threading is supported only on computers that have 3.06-GHz (or higher) microprocessors installed. To determine if your computer is using Hyper-Threading technology: 1. Click the Start button, right-click My Computer, and then click Properties. 2. Click Hardware and click Device Manager. 3. In the Device Manager window, click the plus (+) sign next to the processor type. If Hyper-Threading is enabled, the processor is listed twice. You can enable or disable Hyper-Threading through system setup. For more information on Hyper-Threading, search the Knowledge Base on the Dell Support website at support.dell.com. Back to Contents Page