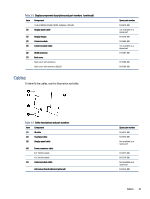
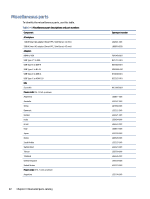
HP 1000-1200 Maintenance and Service Guide 1 - Page 32
Electrostatic discharge information, Generating static electricity
 |
View all HP 1000-1200 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 32 highlights
● Before removing or inserting a hard drive, shut down the computer. If you are unsure whether the computer is off or in Hibernation, turn the computer on, and then shut it down through the operating system. ● Before handling a drive, be sure that you are discharged of static electricity. While handling a drive, avoid touching the connector. ● Before removing an optical drive, be sure that a disc is not in the drive, and be sure that the optical drive tray is closed. ● Handle drives on surfaces covered with at least 2.54 cm (1 inch) of shock-proof foam. ● Avoid dropping drives from any height onto any surface. ● After removing a hard drive or an optical drive, place it in a static-proof bag. ● Avoid exposing an internal hard drive to products that have magnetic fields, such as monitors or speakers. ● Avoid exposing a drive to temperature extremes or liquids. ● If a drive must be mailed, place the drive in a bubble pack mailer or other suitable form of protective packaging, and label the package "FRAGILE." Electrostatic discharge information A sudden discharge of static electricity from your finger or other conductor can destroy static-sensitive devices or microcircuitry. Often the spark is neither felt nor heard, but damage occurs. An electronic device exposed to electrostatic discharge (ESD) might not appear to be affected at all and can work perfectly throughout a normal cycle. The device might function normally for a while, but it has been degraded in the internal layers, reducing its life expectancy. Networks built into many integrated circuits provide some protection, but in many cases, the discharge contains enough power to alter device parameters or melt silicon junctions. IMPORTANT: To prevent damage to the device when you remove or install internal components, observe these precautions: ● Keep components in their electrostatic-safe containers until you are ready to install them. ● Before touching an electronic component, discharge static electricity by using the guidelines described in Personal grounding methods and equipment on page 26. ● Avoid touching pins, leads, and circuitry. Handle electronic components as little as possible. ● If you remove a component, place it in an electrostatic-safe container. Generating static electricity Follow these static electricity guidelines: ● Different activities generate different amounts of static electricity. ● Static electricity increases as humidity decreases. Electrostatic discharge information 25