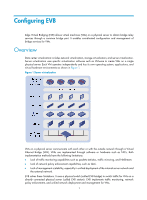
HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch EVB Configuration Guide - Page 7
Configuring LLDP, Specifying a default VSI manager - command reference
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 7 highlights
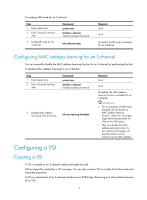
Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enter Ethernet interface view. Command system-view interface interface-type interface-number 3. Enable EVB. evb enable Remarks N/A N/A By default, EVB is disabled on a bridge port. After EVB is enabled, a default access-type S-channel with both SCID and SVID as 1 is automatically created on this port. Configuring LLDP EVB uses LLDP to transmit CDCP TLVs, and CDCP TLVs are carried by the LLDP packet that is addressed using the Nearest non-TPMR Bridge address, so you must configure LLDP. For detailed information about the lldp global enable, lldp enable and lldp agent nearest-nontpmr admin-status commands, see Layer 2-LAN Switching Command Reference. To configure LLDP: Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view 2. Enable LLDP globally. lldp global enable 3. Enter Ethernet interface view. interface interface-type interface-number 4. Enable LLDP on the interface lldp enable 5. Configure the Nearest non-TPMR Bridge agent for lldp agent nearest-nontpmr LLDP to operate in TxRx mode. admin-status txrx Remarks N/A By default, LLDP is disabled globally. N/A By default, LLDP is enabled on a port. The default mode is Disable. Specifying a default VSI manager When the bridge receives a VDP packet other than a De-Associate packet from a station, it contacts the VSI manager specified in the VDP packet to get VSI resources and policies for the station. The VSI manager ID TLV in a VDP packet includes the VSI manager's IP address. If the value for the TLV is all-zero, the VDP packet does not contain a VSI manager's IP address, so the bridge communicates with the specified default VSI manager. To specify a default VSI manager: Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view Remarks N/A 4