HP EVA P6550 HP P6000 EVA Updating Product Software Guide (XCS 11001100) (5697 - Page 26
Identifying virtual disk activity
 |
View all HP EVA P6550 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 26 highlights
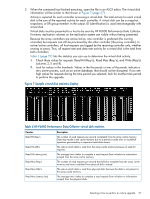
3. Identify instances where IOPS are at a minimum as periods to consider for performing the upgrade. The following configurations and performance levels have been validated by HP for online upgrade of controller software and disk drive firmware. All configurations include the use of HP P6000 Continuous Access. Table 4 Configurations upgraded from XCS 1000x000 and validated by HP Array Number of disks Disk groups Vraid type Total host workload EVA4400 EVA8400 P63x0/P65x0 96 15K RPM disks 324 15K RPM disks 450 10K RPM disks 2 disk groups of 46 disks 2 disk groups of 160 disks 2 disk groups of 223 disks each each each Mix Vraid 1-6 Mix Vraid 1-6 Mix Vraid 1-6 7759 IO/sec total host workload 7583 IO/sec total host workload 9684 IO/sec total host workload NOTE: You can also use the HP TimeLine Visualizer (TLViz) tool to generate graphical representations of performance data. See the HP P6000 Command View User Guide for more information. Identifying virtual disk activity If you cannot identify a period that meets the necessary I/O load requirements, identify those applications that impose heavy I/O loads, and suspend them long enough to perform the upgrade. To do this, use HP P6000 Performance Data Collector to view virtual disk activity. For example, after running HP P6000 Performance Data Collector, you determine that all virtual disks on the array are nearly idle except for one virtual disk. To perform an online upgrade, halt the application that is imposing the load on the busy virtual disk. This will be far less disruptive to your environment than performing an offline upgrade. To view virtual disk activity: 1. Double-click the HP P6000 Performance Data Collector icon on the desktop. The HP P6000 Performance Data Collector command window opens. 2. Enter the following command: evaperf vd -cont n -dur m -sz array -fo filename Select an appropriate interval and duration that will enable you to view a period during which you plan to perform the upgrade. For example, the following command will capture data at 10-minute intervals for 2 hours on an array named EVA1, and store the output in a file named virtual_disks: evaperf vd -cont 600 -dur 7200 -sz EVA1 -fo C:\virtual_disks 26 Preparing for the upgrade