HP NC382m HP Broadcom iSCSI Boot for NC382x Adapters User Guide - Page 8
Option ROM settings - iscsi
 |
View all HP NC382m manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
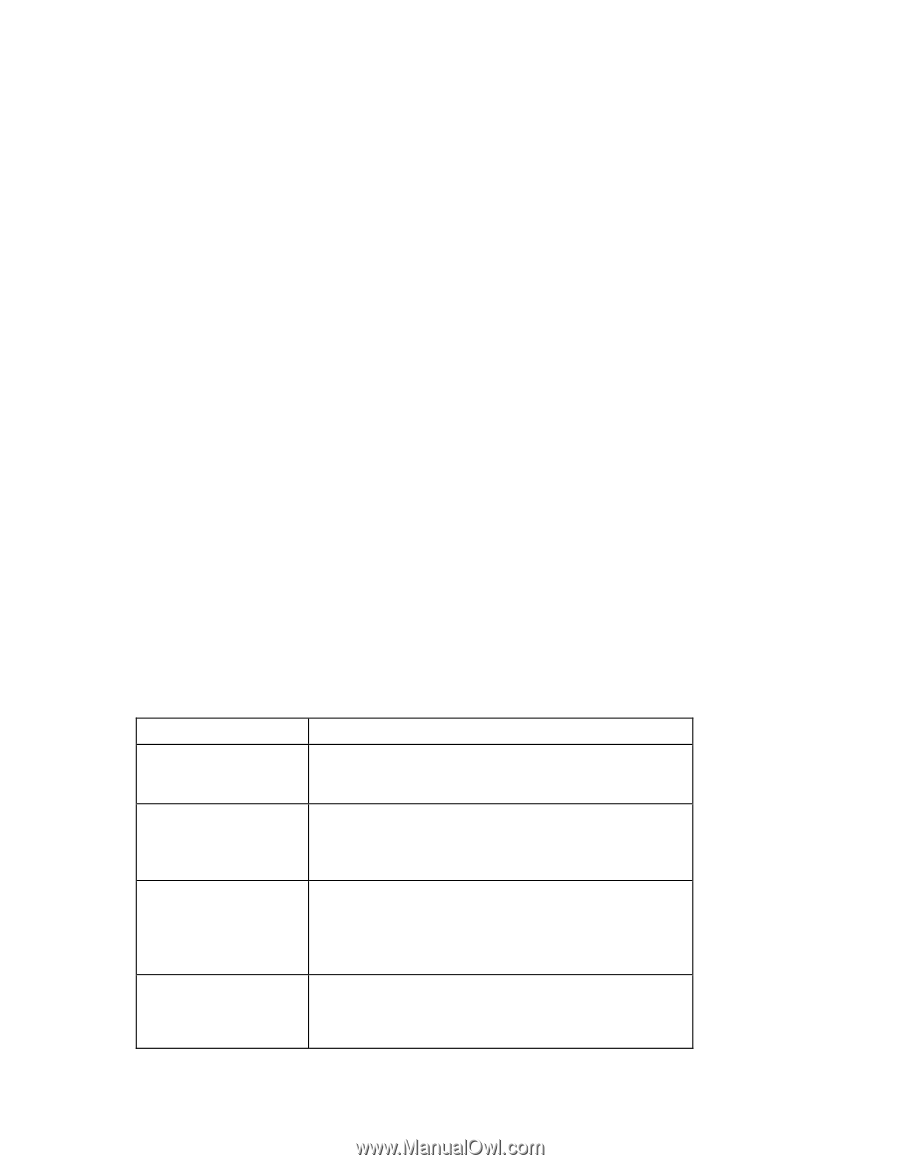
11. Enter values for the Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, Primary DNS, and Secondary DNS parameters as needed. The iSCSI Name corresponds to the iSCSI initiator name to be used by the client system. If authentication is required, enter the CHAP ID and CHAP Secret parameters. 12. Press to return to the Main Menu and then press again to display the Exit Configuration screen and then select Exit and Save the Configurations. Dynamically configure iSCSI parameters In a dynamic configuration the IP address, initiator, and target information is provided by DHCP. 1. Power on the server, and press to launch the MBA Configuration menu when prompted. 2. At the MBA Configuration menu, select the appropriate function key combination to enter the iSCSI Cfg menu. The key combination varies based on your configuration. 3. At the iSCSI Cfg menu, select General Parameters and then select Enabled for the iSCSI parameters via DHCP parameter. 4. For the Boot to iSCSI target parameter, select Disabled to install from a CD/DVD. 5. For the Target as First HDD parameter, select Enabled. 6. For the Windows HBA Boot Mode parameter, select Enabled. 7. Modify the iSCSI Name parameter based on the DHCP options that are used by the DHCP server. o If DHCP Option 17 is used, the initiator name is retrieved from the value entered in the Initiator Parameters screen. But if no value is entered, the controller defaults to the name: iqn.1995-05.com.broadcom..iscsiboot where 11.22.33.44.55.66 is the controller MAC address. o If DHCP Option 43 is used, settings in the Inititator Parameters, 1st Target Parameters, or 2nd Target Parameters fields are ignored and do not need to be cleared. 8. Press to exit and save the settings when prompted. Continue pressing to exit the MBA Configuration Menu. Option ROM settings The following table shows the configuration options available from the General Parameters screen. Variable name TCP/IP parameters via DHCP iSCSI parameters via DHCP CHAP Authentication Boot to iSCSI target Description Determines if the iSCSI boot host software acquires the IP address information using DHCP (Enabled) or use a static IP configuration (Disabled). Determines if the iSCSI boot host software acquires its iSCSI target parameters using DHCP (Enabled) or through a static configuration (Disabled). The static information is entered through the iSCSI Initiator Parameters Configuration screen. Determines if the iSCSI boot host software uses CHAP authentication when connecting to the iSCSI target. If CHAP Authentication is enabled, the CHAP ID and CHAP Secret are entered through the iSCSI Initiator Parameters Configuration screen. Determines if the iSCSI boot host software attempts to boot from the iSCSI target after successfully connecting to it. When the option is enabled, the iSCSI boot host software immediately attempts to boot from the iSCSI target. Otherwise, if it is Installation and configuration 8