HP Server Console 0x2x16 HP IP Console Switch with Virtual Media User Guide - Page 86
Enabling TFTP for Microsoft Windows operating systems
 |
View all HP Server Console 0x2x16 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 86 highlights
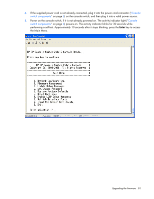
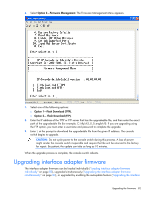
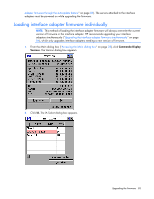
Enabling TFTP for Microsoft Windows operating systems To enable TFTP for Microsoft® Windows® operating systems, follow the instructions in the \TFTP\TFTP Install Instructions.txt file on the CD included with this kit or the Softpaq TFTP directory. Enabling TFTP for Linux operating systems TFTP is provided by the TFTP server RPM (RPM-IVH/Redhat/RPMS/) for most systems using RPM packages. Depending on the type of distribution, the Internet services daemon is provided by xinetd. NOTE: The following example uses Red Hat Linux 3.0. For more information, refer to your Linux operating system Help or documentation. NOTE: By default, TFTP executes in secure mode and only provides readable files under the /tftpboot directory. Other directories can be specified through the /etc/xinetd.d/tftp files. In secure mode, TFTP expects the file to be relative to the/tftpboot directory. To enable TFTP for Linux operating systems (GNOME): 1. In the GNOME viewer go to the main menu and select Programs>System>Service Configuration. 2. In the Service Configuration menu, verify that the xinetd checkbox is selected to start at boot. -orIf the checkbox is not selected, select the box and click Save. 3. Find TFTP in the list of services and highlight it. 4. Select the checkbox to start TFTP at boot, and then click Save. To enable TFTP for Linux operating systems (KDE): 1. Go to the main menu and select Control Panel>Services. 2. In the Service Configuration menu, verify that the xinetd checkbox is selected to start at boot. -orIf the checkbox is not selected, select the box and click Save. 3. Find TFTP in the list of services and highlight it. 4. Select the checkbox to start TFTP at boot, and then click Save. Verifying TFTP for Linux operating systems NOTE: The following example uses Red Hat Linux 3.0. For more information, refer to your Linux operating system Help or documentation. 1. Verify that the in.tftpd service is running with the following ps -ef | grep tftpd. By default the /etc/xinetd.d/tftp configuration file uses /tftpboot as the directory. 2. Create a /tftpboot directory (if it doesn't exist) and set the permissions for public access. 3. Copy the firmware file to /tftpboot. 4. Cd to /tmp. Upgrading the firmware 86