Lenovo ThinkPad 600E Technical Reference Manual for the ThinkPad 600 - Page 43
Real-Time Clock Bytes Hex 000-00D, Status Register A Hex 00A, Interrupt 1AH is the BIOS - bios update
 |
View all Lenovo ThinkPad 600E manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 43 highlights
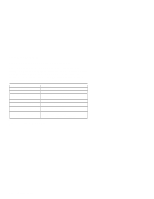
Real-Time Clock Bytes (Hex 000-00D): Bit definitions and addresses for the real-time clock bytes are shown in Figure 2-16. Address (Hex) 000 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 009 00A 00B 00C 00D Function Seconds Second alarm Minutes Minute alarm Hours Hour alarm Day of week Date of month Month Year Status register A Status register B Status register C Status register D Byte Number 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Figure 2-16. Real-Time Clock Bytes (Hex 000-00D) Note: The setup program initializes status registers A and B when the time and date are set. Interrupt 1AH is the BIOS interface to read and set the time and date; it initializes the registers in the same way that the setup program does. Status Register A (Hex 00A) Bit Function 7 Update in progress (UIP) 6-4 Division Chain Select (DVx) 3-0 Rate-selection bits Figure 2-17. Status Register A (Hex 00A) Bit 7 Bits 6-4 Bits 3-0 This bit is a status flag that can be monitored. If this bit is 1, the update transfer will soon occur. If this bit 0, the update transfer will not occur for at least 244 µs. These bits control the divider chain for the oscillator. These bits allow the selection of a divider output frequency or disable the divider output. System Board 2-21