Linksys WRE54G Cisco WAP54GP Wireless-G Exterior Access Point User Guide - Page 10
Planning Your Wireless Network - wireless g range extender
 |
UPC - 745883559046
View all Linksys WRE54G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 10 highlights
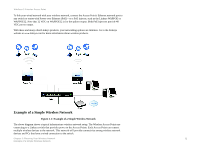
Wireless-G Exterior Access Point Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network Network Topology A wireless network is a group of computers, each equipped with one or more wireless adapters. Computers in a wireless network must be configured to share the same radio channel to talk to each other. Several PCs equipped with wireless cards or adapters can communicate with each other to form an ad-hoc network without the use of an access point. Linksys wireless adapters also provide access to a wired network when using an access point, such as the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point, or wireless router. An integrated wireless and wired network is called an infrastructure network. Each wireless PC in an infrastructure network can talk to any computer in a wired or wireless network via the access point or wireless router. An infrastructure configuration extends the accessibility of a wireless PC to a wired network, and may double the effective wireless transmission range for two wireless adapter PCs. Since an access point is able to forward data within a network, the effective transmission range in an infrastructure network may be doubled (depending on antenna characteristics). ad-hoc: a group of wireless devices communicating directly with each other (peer-to-peer) without the use of an access point. infrastructure: a wireless network that is bridged to a wired network via an access point. Roaming Infrastructure mode also supports roaming capabilities for mobile users. Roaming means that you can move your wireless PC within your network and the access points will pick up the wireless PC's signal, providing that they both share the same wireless channel and SSID. Before you consider roaming, choose a feasible radio channel and optimum access point position. Proper access point positioning combined with a clear radio signal will greatly enhance performance. Note that Spanning Tree Protocol should be disabled on the switches connecting to the APs to allow roaming to work without disruption. roaming: the ability to take a wireless device from one access point's range to another without losing the connection. ssid: your wireless network's name Network Layout The Wireless-G Exterior Access Point has been designed for use with 802.11g and 802.11b products. The Access Point is compatible with 802.11g and 802.11b adapters, such as the Notebook Adapters for your laptop computers, PCI Adapters for your desktop PCs, and USB Adapters for when you want to enjoy USB connectivity. These wireless products can also communicate with a 802.11g or 802.11b Wireless PrintServer. Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network 4 Network Topology