Netgear GS728TP GS728TP/GS728TPP/GS752TP Software Administration Manual - Page 115
MLD Snooping, MLD Snooping Configuration
 |
View all Netgear GS728TP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 115 highlights
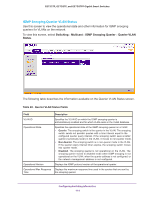
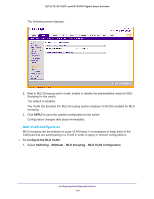
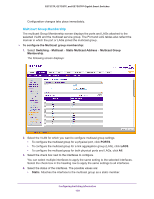
GS752TP, GS728TP, and GS728TPP Gigabit Smart Switches MLD Snooping MLD is a protocol used by IPv6 Multicast routers to discover the presence of multicast listeners (nodes wishing to receive IPv6 multicast packets) on its directly attached links and to discover which multicast packets are of interest to neighboring nodes. MLD is derived from IGMP; MLD version 1 (MLDv1) is equivalent to IGMPv2, and MLD version 2 (MLDv2) is equivalent to IGMPv3. MLD is a sub protocol of Internet Control Message Protocol version 6 (ICMPv6), and MLD messages are a subset of ICMPv6 messages, identified in IPv6 packets by a preceding Next Header value of 58. The switch can snoop on both MLDv1 and MLDv2 protocol packets and bridge IPv6 multicast data based on destination IPv6 multicast MAC addresses. The switch can be configured to perform MLD snooping and IGMP snooping simultaneously. The MLD snooping link contains features described in the following sections: • MLD Snooping Configuration • MLD VLAN Configuration • Multicast Router VLAN Configuration MLD Snooping Configuration In IPv4, Layer 2 switches can use IGMP snooping to limit the flooding of multicast traffic by dynamically configuring Layer 2 interfaces so that multicast traffic is forwarded to only those interfaces associated with IP multicast address. In IPv6, MLD snooping performs a similar function. With MLD snooping, IPv6 Multicast data is selectively forwarded to a list of ports that want to receive the data, instead of being flooded to all ports in a VLAN. This list is constructed by snooping IPv6 multicast control packets. To configure MLD snooping: 1. Select Switching Multicast MLD Snooping MLD Snooping Configuration. Configuring Switching Information 115