Netgear RP614 RP614v4 Reference Manual - Page 46
Configuring LAN TCP/IP Setup Parameters, IP Address., IP Subnet Mask., RIP Direction., RIP Version. - how many devices can it support
 |
UPC - 606449023022
View all Netgear RP614 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 46 highlights
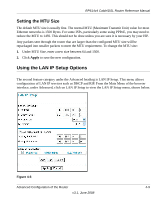
RP614v4 Cable/DSL Router Reference Manual Configuring LAN TCP/IP Setup Parameters The router is shipped preconfigured to use private IP addresses on the LAN side, and to act.as a DHCP server. The router's default LAN IP configuration is: • LAN IP addresses-192.168.1.1 • Subnet mask-255.255.255.0 These addresses are part of the IETF-designated private address range for use in private networks, and should be suitable in most applications. If your network has a requirement to use a different IP addressing scheme, you can make those changes in this menu. The LAN IP parameters are: • IP Address. This is the LAN IP address of the router. Note: If you change the LAN IP address of the router while connected through the browser, you will be disconnected. You must then open a new connection to the new IP address and log in again. • IP Subnet Mask. This is the LAN Subnet Mask of the router. Combined with the IP address, the IP Subnet Mask allows a device to know which other addresses are local to it, and which must be reached through a gateway or router. • RIP Direction. RIP (Router Information Protocol) allows a router to exchange routing information with other routers. The RIP Direction selection controls how the router sends and receives RIP packets. Both is the default. - When set to Both or Out Only, the router will broadcast its routing table periodically. - When set to Both or In Only, it will incorporate the RIP information that it receives. - When set to None, it will not send any RIP packets and will ignore any RIP packets received. • RIP Version. This controls the format and the broadcasting method of the RIP packets that the router sends. (It recognizes both formats when receiving.) By default, this is set for RIP-1. - RIP-1 is universally supported. RIP-1 is probably adequate for most networks, unless you have an unusual network setup. - RIP-2 carries more information. RIP-2B uses subnet broadcasting. 4-10 Advanced Configuration of the Router v3.1, June 2008