Olympus LS-100 LS-100 Instruction Manual (English) - Page 128
Glossary - digital recorder
 |
View all Olympus LS-100 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
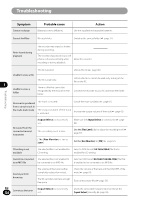
Page 128 highlights
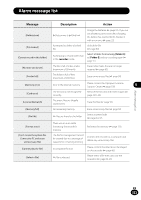
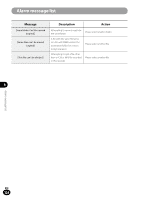
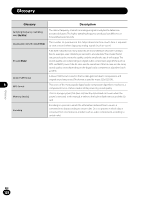
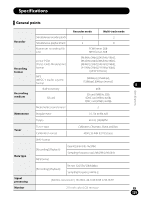
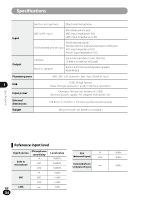
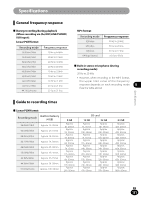
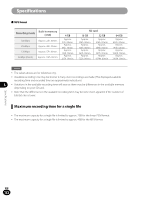
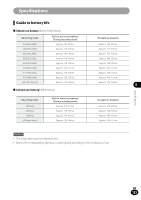
Glossary Glossary Description Sampling frequency (sampling rate) [Hz/kHz] The rate or frequency at which an analogue signal is analyzed to determine acoustic delicacies. The higher sampling frequency produces less difference in forward/backward sounds. The number of quantization bits helps determine how much data is required Quantization bits [bit depth][bit] to save a record when digitizing analog signals (such as voice). Bit rate [kbps] A Bit Rate indicates how many data bits are transmitted per second.A 128 kbps file, for example, uses 128 kbits per second to encode data. The smaller the bit rate you select, the worse the quality, and the smaller the size it will output. The sound quality varies depending on digital audio compression algorithms (such as MP3 and WMA), even if the bit rates are the same.Even if the bit rates are the same, sound quality varies depending on the digital audio compression algorithm (such as MP3). Linear PCM format 8 MP3 format A linear PCM format is used so that no data gets lost due to compression and original sound stays intact.This format is used for music CDs (CD-DA). This is one of the most popular digital audio compression algorithms. It achieves a compression factor of about twelve while preserving sound quality. Glossary Memory (media) This is a storage system that does not lose the data stored on it even when the power is removed. In this manual, it refers to the built-in flash memory and the SD card. Encoding Encoding is a process in which the information obtained from a source is converted into data according to certain rules. Or it is a process in which data is converted from one format to another (such as audio compression) according to certain rules. EN 128