Seagate ST800FM0022 Pulsar.2 SAS Product Manual - Page 15
Thin Provisioned LBA
 |
View all Seagate ST800FM0022 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
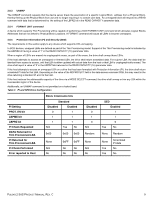
3.8.3 UNMAP The UNMAP command requests that the device server break the association of a specific Logical Block address from a Physical Block, thereby freeing up the Physical Block from use and no longer requiring it to contain user data. An unmapped block will respond to a READ command with data that is determined by the setting of the LBPRZ bit in the READ CAPACITY parameter data. 3.8.4 FORMAT UNIT command A device which supports Thin Provisioning will be capable of performing a SCSI FORMAT UNIT command which allocates Logical Blocks Addresses that are not linked to Physical Block Locations. A FORMAT command will cause all LBAs to become unmapped. 3.8.5 Protection Information (PI) and Security (SED) The requirements in this section apply to any device which supports LBA unmapping. In SCSI devices, umapped LBAs are defined as part of the Thin Provisioning model. Support of the Thin Provisioning model is indicated by the LBPME bit having a value of '1' in the READ CAPACITY (16) parameter data. When a region of LBA's are erased via cryptographic erase, as part of the erase, the drive shall unmap those LBAs. If the host attempts to access an unmapped or trimmed LBA, the drive shall return scrambled data. For a given LBA, the data shall be identical from access to access, until that LBA is either updated with actual data from the host or that LBA is cryptographically erased. The drive shall report a value of '0' in the LBPRZ field returned in the READ CAPACITY (16) parameter data. If the host attempts to access an unmapped LBA on a drive that has been formatted with Protection Information (PI), the drive shall return scrambled PI data for that LBA. Depending on the value of the RDPROTECT field in the data-access command CDB, this may result in the drive returning a standard PI error to the host. If the host reduces the addressable capacity of the drive via a MODE SELECT command, the drive shall unmap or trim any LBA within the inaccessible region of the device. Additionally, an UNMAP command is not permitted on a locked band. Table 3 PI and SED Drive Configuration PI Setting PROT_EN bit LBPME bit LBPRZ bit PI Check Requested DATA Returned for Thin Provisioned LBA PI Returned for Thin Provisioned LBA PI Check Performed Error reported to Host DRIVE CONFIGURATION Standard Disabled Enabled 0 1 1 1 1 1 N/A Yes No 0x00 0x00 0x00 None N/A No 0xFF No No 0xFF No No Disabled 0 1 0 N/A SED Enabled 1 1 0 Yes No Random None Random None N/A No None Yes Yes Scrambled PI data No No PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 9