Seagate ST800FM0022 Pulsar.2 SAS Product Manual - Page 54
MODE SENSE data - hard drive
 |
View all Seagate ST800FM0022 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 54 highlights
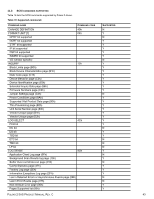
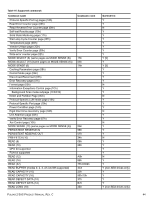
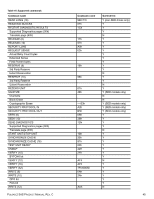
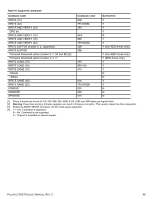
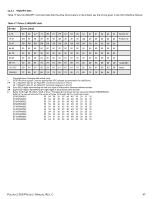
11.3.2 MODE SENSE data The MODE SENSE command provides a way for the drive to report its operating parameters to the initiator. The drive maintains four sets of mode parameters: 1. Default values Default values are hard-coded in the drive firmware stored in flash E-PROM (nonvolatile memory) on the drive's PCB. These default values can be changed only by downloading a complete set of new firmware into the flash E-PROM. An initiator can request and receive from the drive a list of default values and use those in a MODE SELECT command to set up new current and saved values, where the values are changeable. 2. Saved values Saved values are stored on the drive's media using a MODE SELECT command. Only parameter values that are allowed to be changed can be changed by this method. Parameters in the saved values list that are not changeable by the MODE SELECT command get their values from default values storage. When power is applied to the drive, it takes saved values from the media and stores them as current values in volatile memory. It is not possible to change the current values (or the saved values) with a MODE SELECT command before the drive is "ready." An attempt to do so results in a "Check Condition" status. On drives requiring unique saved values, the required unique saved values are stored into the saved values storage location on the media prior to shipping the drive. Some drives may have unique firmware with unique default values also. On standard OEM drives, the saved values are taken from the default values list and stored into the saved values storage location on the media prior to shipping. 3. Current values Current values are volatile values being used by the drive to control its operation. A MODE SELECT command can be used to change the values identified as changeable values. Originally, current values are installed from saved or default values after a power on reset, hard reset, or Bus Device Reset message. 4. Changeable values Changeable values form a bit mask, stored in nonvolatile memory, that dictates which of the current values and saved values can be changed by a MODE SELECT command. A one (1) indicates the value can be changed. A zero (0) indicates the value is not changeable. For example, in Table 19, refer to Mode page 81, in the row entitled "CHG." These are hex numbers representing the changeable values for Mode page 81. Note in columns 5 and 6 (bytes 04 and 05), there is 00h which indicates that in bytes 04 and 05 none of the bits are changeable. Note also that bytes 06, 07, 09, 10, and 11 are not changeable, because those fields are all zeros. In byte 02, hex value FF equates to the binary pattern 11111111. If there is a zero in any bit position in the field, it means that bit is not changeable. Since all of the bits in byte 02 are ones, all of these bits are changeable. The changeable values list can only be changed by downloading new firmware. Note. Because there are often several different versions of drive control firmware in the total population of drives in the field, the MODE SENSE values given in the following tables may not exactly match those of some drives. The following tables list the values of the data bytes returned by the drive in response to the MODE SENSE command pages for SCSI implementation (see the SAS Interface Manual ). DEF = Default value. Standard OEM drives are shipped configured this way. CHG = Changeable bits; indicates if default value is changeable. PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 48