Sony DSC-RX100M5 Picture Profile: Help Guide for Creators (Printable PDF) - Page 18
Adjusting coloring Saturation/Color Phase/Color Depth - manual
 |
View all Sony DSC-RX100M5 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 18 highlights
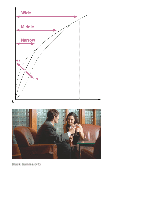
[Point] sets the position of the knee point output level. [Slope] determines the inclination of the knee slope. A negative slope setting results in a gentler knee slope angle. This expands the dynamic range, but reduces the ability to produce rich gradations. A positive slope setting makes the knee slope inclination steeper. This shrinks the dynamic range, but bolsters the ability to express gradations. When [Slope] is set to +5, the Knee function is disabled. Set [Point] and [Slope] in [Manual Set] in combination. If you select a higher setting for [Point] and a gentler setting for [Slope], you can obtain video-like sharp highlight effects. If softer film-like highlight effects are desired, select a lower setting for [Point] and a steeper setting for [Slope]. In practical terms, move [Point] and [Slope] up and down in opposite directions while checking the gradations in high luminance areas until you find the ideal settings. [8] Picture Profile setting parameters Adjusting coloring (Saturation/Color Phase/Color Depth) Saturation This function adjusts the color saturation. Parameters Settings Saturation -32 (fainter in color) to +32 (richer in color) A positive value results in more vivid colors, while a negative value presents faded colors. Saturation must be adjusted in tandem with contrast. Bright and vivid settings produce videolike images, while dark and vivid settings result in film-like images. The combination of bright and light creates pastel tones, whereas dark and light settings create artistic finishes. Color Phase This function adjusts the color hue. Parameters Settings Color Phase -7 (Greenish) to +7 (Reddish) As you rotate the color wheel to the left (decreasing the set value) or to the right (increasing the set value), the colors shift along the spectrum from red to yellow, green, cyan, blue, magenta and red. Because this affects all colors, it is difficult to make specific adjustments exactly as intended. Use this function when matching coloring closely between different cameras.