TP-Link TD-W8960N User Guide - Page 32
Use the following IP Address, gateway IP Address - wireless manual
 |
UPC - 845973060343
View all TP-Link TD-W8960N manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 32 highlights
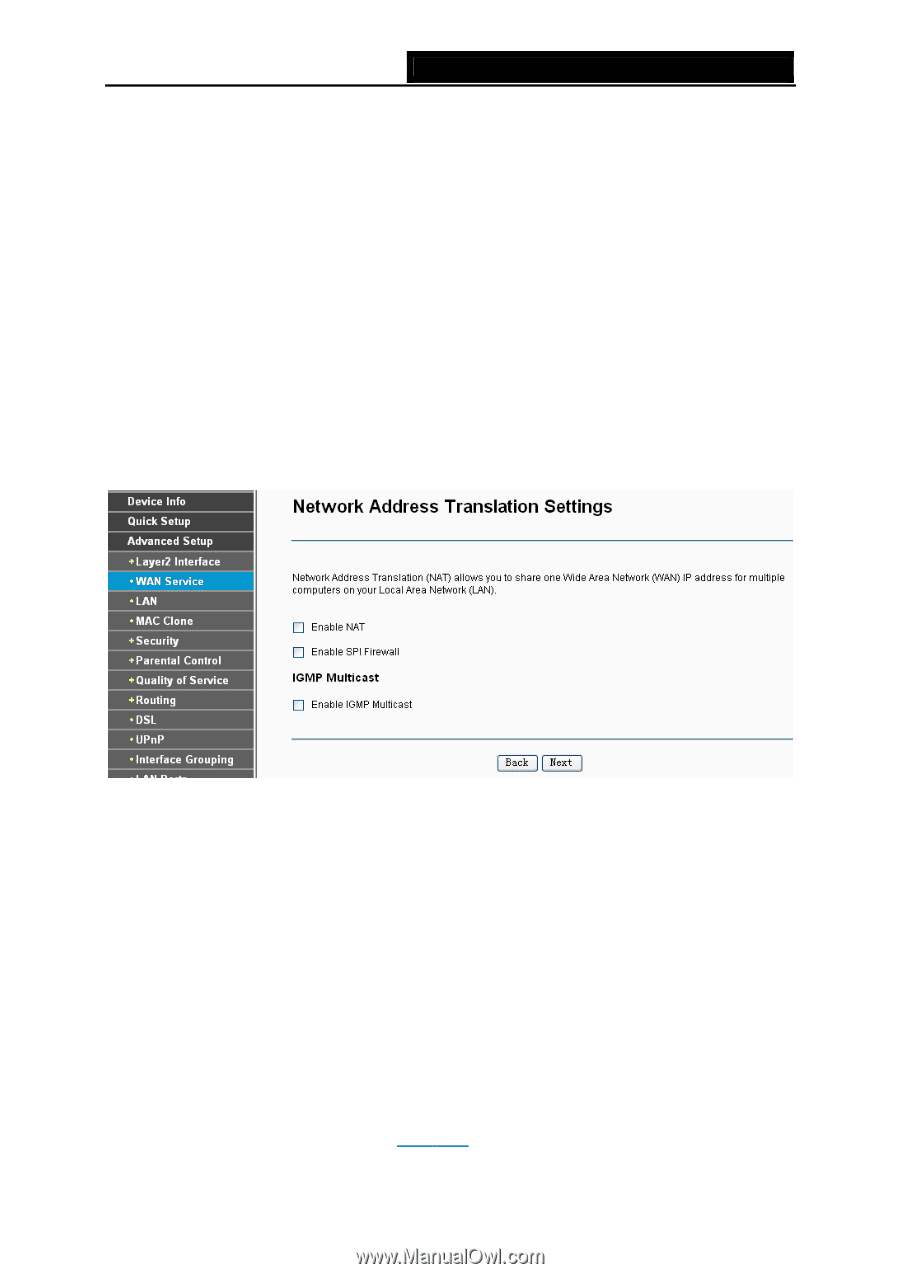
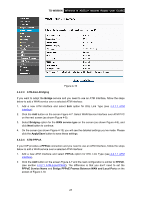
TD-W8960N Wireless N ADSL2+ Modem Router User Guide the first identity and be incremented for each subsequent identity. For example, the device may use IAID value 1 for the first physical interface and value 2 for the second. Alternatively, the device may use IAID value 1 for the virtual circuit corresponding to the first connection object in the data model and value 2 for the second connection object in the data model. • Option 61 DUID: Specifies the name of the interface whose link-layer address the server is to use as its DUID (DHCP Unique Identifier). You must enter a value for this parameter or the server will not start. When the server starts, the DUID is written to the system log. • Option 125: The option 125 allows DHCP server to be pre-configured with policy for handling classes of devices in a certain way without requiring DHCP server to be able to parse the unique format used in client-identifier option. ¾ Use the following IP Address: If you are provided with a static IP/gateway Address, please select this option, and then enter the WAN IP Address, WAN Subnet Mask and WAN gateway IP Address manually. 5. You will see the next screen as below. You can enable the NAT, SPI Firewall, and IGMP Multicast, if you are not sure about the settings, just leave the default settings. Click Next. Figure 4-16 ¾ Enable NAT: This technology translates the IP addresses of a local area network to a different IP address for the Internet. If this Router is hosting your network's connection to the Internet, please select the check box. If another Router exists in your network, you don't need to select the option. ¾ Enable SPI Firewall: A SPI firewall enhances network's security. Select the option to use a firewall, or else without a firewall. ¾ Enable IGMP Multicast: This is disabled by default. This setting will not allow IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) packets to be forwarded to the LAN. IGMP is used to manage multicasting on TCP/IP networks. Most users will not need to enable this. Some ISPs use IGMP to perform remote configuration for client devices, such as the Router. If you are unsure, check with your ISP. ) Note: If you select the Enable NAT checkbox, the NAT menu will be added to the Web-based Utility. We will describe the detailed configuration in 4.4.5 NAT. 25