ZyXEL G-200 User Guide - Page 30
WPA improves data encryption by using Temporal Key Integrity Protocol TKIP, Message
 |
View all ZyXEL G-200 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
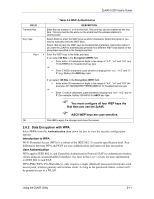
ZyAIR G-200 User's Guide Encryption WPA improves data encryption by using Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), Message Integrity Check (MIC) and IEEE 802.1x. Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) uses 128-bit keys that are dynamically generated and distributed by the authentication server. It includes a per-packet key mixing function, a Message Integrity Check (MIC) named Michael, an extended initialization vector (IV) with sequencing rules, and a re-keying mechanism. TKIP regularly changes and rotates the encryption keys so that the same encryption key is never used twice. The RADIUS server distributes a Pairwise Master Key (PMK) key to the AP that then sets up a key hierarchy and management system, using the pair-wise key to dynamically generate unique data encryption keys to encrypt every data packet that is wirelessly communicated between the AP and the wireless clients. This all happens in the background automatically. The Message Integrity Check (MIC) is designed to prevent an attacker from capturing data packets, altering them and resending them. The MIC provides a strong mathematical function in which the receiver and the transmitter each compute and then compare the MIC. If they do not match, it is assumed that the data has been tampered with and the packet is dropped. By generating unique data encryption keys for every data packet and by creating an integrity checking mechanism (MIC), TKIP makes it much more difficult to decode data on a Wi-Fi network than WEP, making it difficult for an intruder to break into the network. The encryption mechanisms used for WPA and WPA-PSK are the same. The only difference between the two is that WPA-PSK uses a simple common password, instead of user-specific credentials. The common-password approach makes WPA-PSK susceptible to brute-force password-guessing attacks but it's still an improvement over WEP as it employs an easier-to-use, consistent, single, alphanumeric password. Figure 2-11 WPA Authentication Follow the instructions in the table to configure WPA security. 2-12 Using the ZyAIR Utility