ZyXEL M-102 User Guide - Page 74
User Authentication, WPA2-PSK Application Example
 |
View all ZyXEL M-102 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 74 highlights
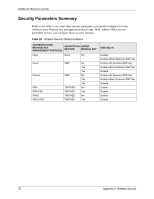
ZyXEL M-102 User's Guide The Message Integrity Check (MIC) is designed to prevent an attacker from capturing data packets, altering them and resending them. The MIC provides a strong mathematical function in which the receiver and the transmitter each compute and then compare the MIC. If they do not match, it is assumed that the data has been tampered with and the packet is dropped. By generating unique data encryption keys for every data packet and by creating an integrity checking mechanism (MIC), with TKIP and AES it is more difficult to decrypt data on a Wi-Fi network than WEP and difficult for an intruder to break into the network. The encryption mechanisms used for WPA(2) and WPA(2)-PSK are the same. The only difference between the two is that WPA(2)-PSK uses a simple common password, instead of user-specific credentials. The common-password approach makes WPA(2)-PSK susceptible to brute-force password-guessing attacks but it's still an improvement over WEP as it employs a consistent, single, alphanumeric password to derive a PMK which is used to generate unique temporal encryption keys. This prevent all wireless devices sharing the same encryption keys. (a weakness of WEP) User Authentication WPA and WPA2 apply IEEE 802.1x and Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) to authenticate wireless stations using an external RADIUS database. WPA2 reduces the number of key exchange messages from six to four (CCMP 4-way handshake) and shortens the time required to connect to a network. Other WPA2 authentication features that are different from WPA include key caching and pre-authentication. These two features are optional and may not be supported in all wireless devices. Key caching allows a wireless client to store the PMK it derived through a sucessful authentication with an AP. The wireless client uses the PMK when it tries to connect to the same AP and does not need to go with the authentication process again. Pre-authentication enables fast roaming by allowing the wireless client (already connecting to an AP) to perform IEEE 802.1x authentication with another AP before connecting to it. WPA(2)-PSK Application Example A WPA(2)s-PSK application looks as follows. 1 First enter identical passwords into the AP and all wireless clients. The Pre-Shared Key (PSK) must consist of between 8 and 63 ASCII characters or 64 hexadecimal characters (including spaces and symbols). 2 The AP checks each client's password and (only) allows it to join the network if it matches its password. 3 The AP and wireless clients use the pre-shared key to generate a common PMK. 4 The AP and wireless clients use the TKIP or AES encryption process to encrypt data exchanged between them. 74 Appendix C Wireless Security