ZyXEL NBG-418N User Guide - Page 78
Quality of Service QoS Screen
 |
View all ZyXEL NBG-418N manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 78 highlights
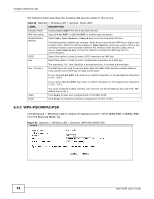
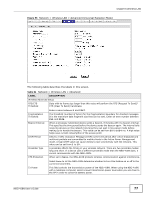
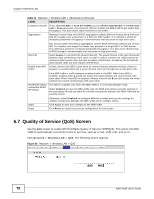
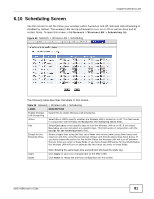
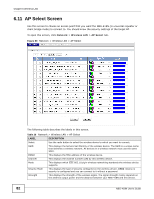
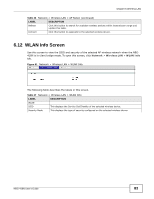
Chapter 6 Wireless LAN Table 31 Network > Wireless LAN > Advanced (continued) LABEL Extension Channel Aggregation DESCRIPTION If you select 40 MHz or Auto 20/40MHz as your Channel Bandwidth in the Wireless LAN > General screen, the extension channel enables the NBG-419N to get higher data throughput. This also lowers radio interference and traffic. Message Protocol Data Unit (MPDU) aggregation collects Ethernet frames along with their 802.11n headers and wraps them in a 802.11n MAC header. This method is useful for increasing bandwidth throughput in environments that are prone to high error rates. Short GI Enable Intra-BSS Traffic Mac Service Data Unit (MSDU) aggregation collects Ethernet frames without any of their 802.11n headers and wraps the header-less payload in a single 802.11n MAC header. This method is useful for increasing bandwidth throughput. It is also more efficient than A-MPDU except in environments that are prone to high error rates. Select Enable to use Short GI (Guard Interval). The guard interval is the gap introduced between data transmission from users in order to reduce interference. Reducing the GI increases data transfer rates but also increases interference. Increasing the GI reduces data transfer rates but also reduces interference. A Basic Service Set (BSS) exists when all communications between wireless clients or between a wireless client and a wired network client go through one access point (AP). WLAN STA setting overwrites WLAN AP setting Intra-BSS traffic is traffic between wireless clients in the BSS. When Intra-BSS is enabled, wireless client A and B can access the wired network and communicate with each other. When Intra-BSS is disabled, wireless client A and B can still access the wired network but cannot communicate with each other. This field is available only when the NBG-418N is in universal repeater mode. Select Enabled to have the NBG-418N copy the SSID and wireless security settings of the associated AP, and use them for wireless connections between the NBG-418N and its wireless clients. Apply Reset Otherwise, select Disabled to configure different wireless and security settings for wireless connections between the NBG-418N and its wireless clients. Click Apply to save your changes to the NBG-418N. Click Reset to reload the previous configuration for this screen. 6.7 Quality of Service (QoS) Screen Use the QoS screen to enable Wifi MultiMedia Quality of Service (WMMQoS). This allows the NBG418N to automatically set priority levels to services, such as e-mail, VoIP, chat, and so on. Click Network > Wireless LAN > QoS. The following screen appears. Figure 56 Network > Wireless LAN > QoS 78 NBG-418N User's Guide