Casio FC-200V User Guide - Page 101
Hyperbolic and Inverse Hyperbolic, Functions, Converting an Input Value to the, Calculator's Default
 |
UPC - 079767167004
View all Casio FC-200V manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
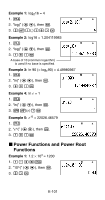
Page 101 highlights
Example: sin 30 = 0.5, sin-10.5 = 30 z 11(sin)30)E 1. t 2. "sin-1" (fc), then E. 3. 0.5)E k Hyperbolic and Inverse Hyperbolic Functions Example: sinh 1 = 1.175201194, cosh-1 1 = 0 1. t 2. "sinh" (fc), then E. 3. 1)E 1. t 2. "cosh-1" (fc), then E. 3. 1)E k Converting an Input Value to the Calculator's Default Angle Unit After inputting a value, press 1G(DRG') to display the angle unit specification menu shown below. Press the number key that corresponds to the angle unit of the input value. The calculator will automatically convert it to the calculator's default angle unit. Example 1: To convert the following values to degrees: π radians = 90°, 50 grads = 45° 2 The following procedure assumes that the calculator's default angle unit is degrees. E-99