Dell PowerVault 221S Optimizing Dell SCSI Solutions - Page 10
I/O Profile, Read/Write, Sequential/Random, Bandwidth, IO Size, Latency, Sensitivity, Growth,
 |
View all Dell PowerVault 221S manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 10 highlights
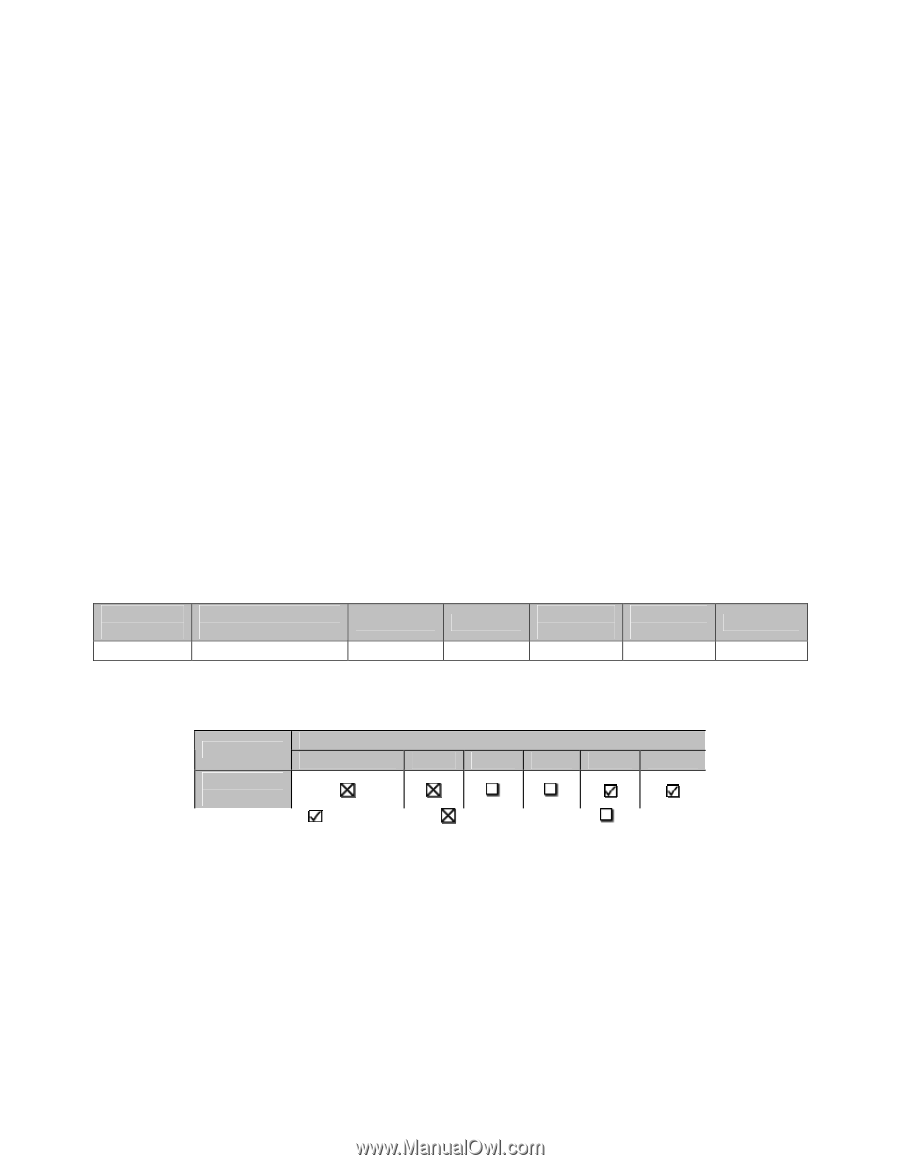
A REFERENCE GUIDE FOR OPTIMIZING DELL™ SCSI SOLUTIONS VER A02 • RAID 50 - Recommended for those solutions that require a balance between storage capacity and performance. Possible: • RAID 1 - Possible solution for situations which do not require high storage capacity. Not recommended: • RAID 0, Concatenated - These are not recommended due to lack of redundancy and data protection. Note: While these configurations are not recommended, they can be configured and utilized. File Servers File servers can be archival long term storage repositories or more dynamic user file storage where files are changed, added and deleted on a daily basis. They can range from workgroup to company level in their scope. A key factor for file servers is storage capacity as users add more files. File servers are generally not mission critical systems so reduced availability and redundancy or none at all is acceptable as the data is usually backed up and can be restored in a matter of hours. Archival file server characteristics and recommendations • Table 2-11 Archival File Server General I/O profile I/O Profile I/O Profile (Read/Write) (Sequential/Random) Bandwidth 90/10 Sequential Moderate IO Size >64K Latency Sensitivity High Growth Rate Varies Criticality Low • Table 2-12: Archival File Server RAID Guidelines Application File Archival Concatenated 0 Recommended RAID Level 1 10 Not Recommended 5 50 Possible Recommended: • RAID 10 - Recommended due to the high availability and redundancy and good performance. • RAID 5 - Recommended for file servers that require maximum storage capacity and only base data protection and performance. • RAID 50 - Recommended for those solutions that require a balance between storage capacity and performance. Possible: PAGE 10 11/17/2005