Dell PowerVault 221S Optimizing Dell SCSI Solutions - Page 34
Interface Channel Options - Internal/External/Multi channel device configuration
 |
View all Dell PowerVault 221S manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 34 highlights
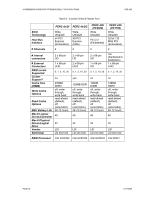
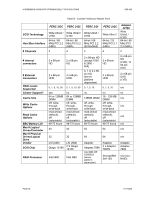
A REFERENCE GUIDE FOR OPTIMIZING DELL™ SCSI SOLUTIONS VER A02 drives supported by the PV22xS). Mixing spindle speeds within the same array will impact array performance, especially in a striped (RAID0, RAID10 or RAID50) environment. Higher RPM drives will have to wait for the slower ones to complete the operations. This is the case regardless of cache policy settings. Interface Channel Options - Internal/External/Multi channel device configuration • See Table 5-2 for internal/external connector details for each controller. • Do not connect devices both internally and externally on any one channel. • Termination o The PV22xS is also already terminated. No external SCSI bus terminators are needed when connecting to a PV22xS. • Spanning of Arrays Dell's PERC controllers provide additional array configuration options of spanning logical arrays. Dell supports spanning of logical arrays only across multiple channels on same PERC controllers. If multiple PV22xS are configured (Joined or Split topology - Figure 4-3a) on the same PERC then a logical array may be spanned across multiple PV22xS. In general, spanning of logical arrays across multiple channels on a controller improves data throughput. With the introduction of another data path, depending on the RAID level, the configuration may compromise data availability. When configuring logical arrays across multiple channels it is essential to understand the trade-off between performance, reliability and availability of data. Depending on the RAID level for an array, spanning may offer a better solution than without spanning. The following table lists pros and cons of spanning in relation to RAID levels: PAGE 34 11/17/2005