Dell PowerVault 221S Optimizing Dell SCSI Solutions - Page 6
I/O Profile - support
 |
View all Dell PowerVault 221S manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
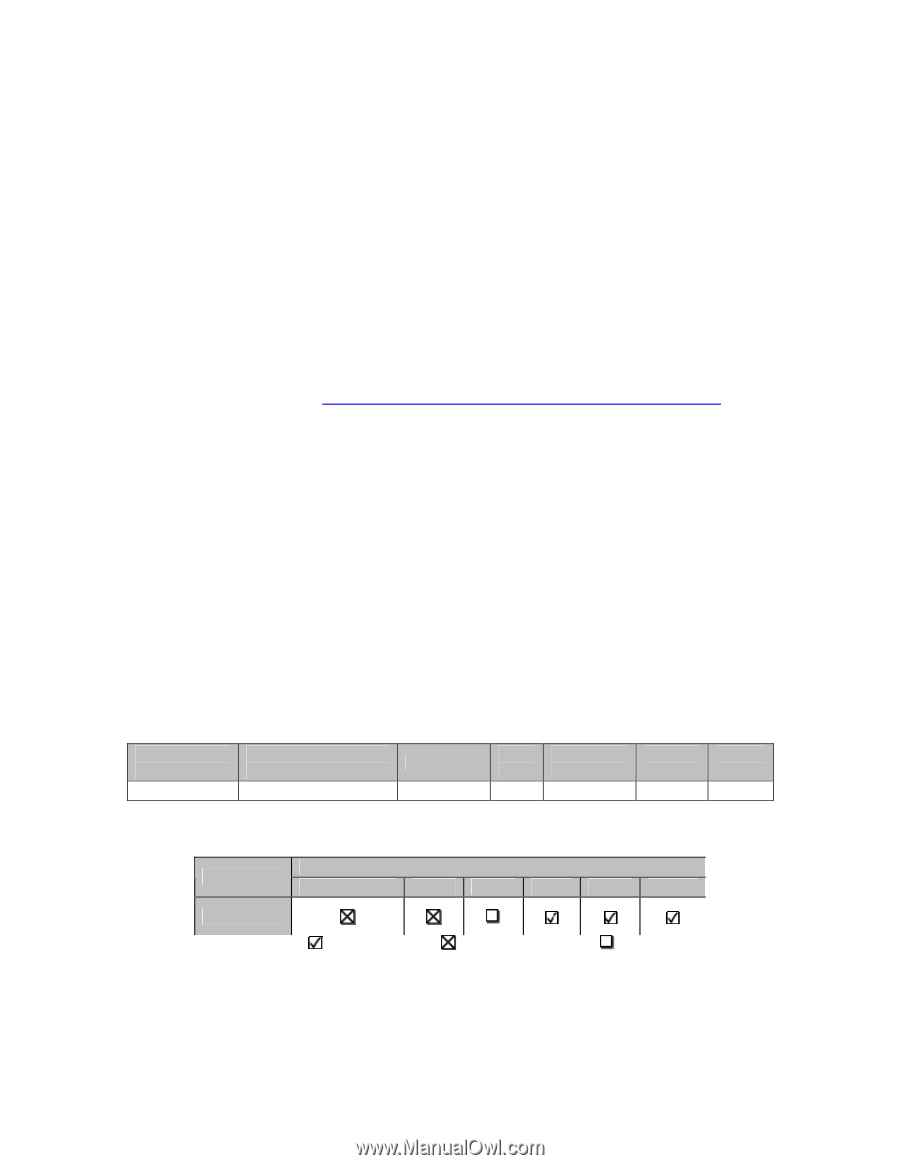
A REFERENCE GUIDE FOR OPTIMIZING DELL™ SCSI SOLUTIONS VER A02 RAID 5 RAID 5 has good I/O performance, data protection and relative cost with excellent storage capacity. RAID 5 should be used in situations where maximum storage capacity is required along with a moderate amount of data protection. RAID 50 A balance between RAID 5 and RAID 10, this solution offers good I/O performance, availability and good storage capacity. This configuration offers slightly higher performance than RAID 5, but at a slightly higher cost and reduced storage capacity. It does however provide greater storage capacity than a RAID 10 solution with a decrease in performance and data protection. This should be used in situations where greater redundancy and data protection is required as well as reasonable storage capacity. Note: For more details on RAID configurations refer to the Dell™ 'Getting Started with RAID' document (http://support.dell.com/support/edocs/storage/RAID/RAIDbk0.pdf). Concatenated Container This solution is not recommended due to lack of data protection and redundancy and no performance gain. However for non-critical implementations that require high scalability this type of solution will provide more ease of use than other RAID configurations. Application specific guidelines E-Mail Servers The storage requirements for e-mail servers can vary depending on the size, the amount, and type of users. While small departmental e-mail servers may work well with a small amount of storage and limited features; large corporate e-mail servers normally require greater storage capacity, very high availability, performance and scalability. IO profiles will vary depending on the number of users and type of mail and attachments sent. • Table 2-3: Email Server General I/O profile I/O Profile (Read/Write) 60/40 I/O Profile (Sequential/Random) Bandwidth Random Heavy I/O Size 4k Latency Sensitivity High Growth Rate High Critical ity High • Table 2-4: Email Sever RAID Guidelines Application E-Mail Concatenated 0 Recommended RAID Level 1 10 Not Recommended 5 50 Possible Recommended: PAGE 6 11/17/2005