Dell PowerVault 221S Optimizing Dell SCSI Solutions - Page 29
SCSI Host Bus Adapters / SCSI RAID - driver
 |
View all Dell PowerVault 221S manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 29 highlights
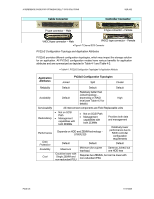
A REFERENCE GUIDE FOR OPTIMIZING DELL™ SCSI SOLUTIONS VER A02 5. SCSI Host Bus Adapters / SCSI RAID This section addresses concerns specific to RAID. A summarized table (Table 5-2) is presented at the end of the section which provides an overview of the Dell SCSI and RAID solutions that support PV22xS. Although attachment of PV22xS to 39160 SCSI HBA is supported, it is not recommended. 39160 is a U160 SCSI HBA, which is primarily intended for SCSI Tape devices, and would limit the performance of SCSI subsystem to U160 speeds. The controller doesn't provide any hardware RAID benefits similar to software RAID. RAID: Hardware Vs Software A RAID system mostly provides a fail-safe with the capability of improved performance data storage on a group of hard disk drives. RAID, when implemented with a hardware engine - including a dedicated RAID processor and memory system - is termed a hardware RAID. Whereas, when the RAID engine is implemented on a host processor and memory - either as part of operating system or driver, it is termed a software RAID. Hardware and Software RAID implementations are associated with their respective pros and cons. The fact that the Hardware RAID is implemented using dedicated hardware resources gives a performance boost to the host systems which are required to perform heavy data processing. Software RAID performance scales based on the available memory and processing resources for a given host system. Thus, host systems which are used for heavy data processing will exhibit slower performance with Software RAID when compared to Hardware RAID implementations. Selection of Hardware RAID vs Software RAID is a trade-off between performance and cost. Enterprise host systems which perform heavy data processing and are mission critical would be more suited for a Hardware RAID implementation. For more details on Hardware and Software RAID please refer to "Comparing RAID Implementation Methods" and "Implementing Software RAID on Dell PowerEdge Servers" papers in Appendix - A: References. Considerations to Implement a RAID Solution Implementing a RAID solution requires that certain considerations be addressed in order to achieve an optimum solution. These considerations are impacted by: • Controller Family • Data Protection Strategy • High Availability Needs - Clustering • Heterogeneous vs Homogeneous Environment - SCSI bus technology (U160/U320) and Hard Disk Drive (HDD) spindle speeds • Interface Channel options - Internal and External channels o Spanning across channels/controllers/PV22xS • Capacity Needs - Virtual Disk Size Each of these above factors is discussed in detail in following sections. PAGE 29 11/17/2005