HP DL360 The Intel processor roadmap for industry-standard servers technology - Page 17
Three-level cache hierarchy
 |
UPC - 613326948835
View all HP DL360 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 17 highlights
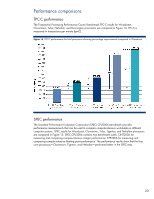
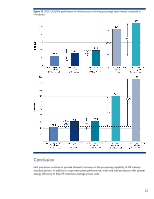
Three-level cache hierarchy Each Intel Xeon 5500 series processor has a three-level cache hierarchy (Figure 11): • An on-die, 64-kilobyte, L1 cache that is split into two 32-kilobyte caches storing data and instructions • An individual, 256-kilobyte, L2 cache for each core for lower latency • A new inclusive, fully shared, Level 3 (L3) cache that can be up to 8 megabytes The L3 cache is shared and inclusive, which means that it duplicates the data stored in the L1 and L2 caches of each core. This guarantees that data is stored outside the cores, thus minimizing latency by eliminating unnecessary core snoops to the L1 and L2 caches. The L3 cache has additional flags that track which core's cache supplied the original data. Therefore, if one core modifies the data of another core in L3 cache, the L1 and L2 caches of the core that originated the data are updated. This eliminates excessive inter-core traffic and ensures multi-level cache coherence. Figure 11. Three-level cache hierarchy in the Intel Xeon 5500 series processors Table 5. 60-Watt, 80-Watt, and 95-Watt Intel Xeon 5500 series processor specifications Turbo Boost 60W L5530 (2.40 GHz) L5520 (2.26 GHz) 8MB L3, 5.86 GT/s QPI, 800/1066 MHz DDR3, HyperThreading L5506 (2.13 GHz) 4MB L3, 4.8 GT/s QPI, 800 MHz DDR3, No HyperThreading 80W E5540 (2.53 GHz) E5530 (2.40 GHz) E5520 (2.26 GHz) 8MB L3 5.86 GT/s QPI 1066 MHz DDR3 HyperThreading E5506 (2.13 GHz) E5504 (2.00 GHz) E5502 (1.86 GHz) 4MB L3 4.8 GT/s QPI 800 MHz DDR3 No HyperThreading 95W E5570 (2.93 GHz) E5560 (2.80 GHz) 8MB L3 6.40 GT/s QPI 800/1066/1333 MHz DDR3 Hyper-Threading E5550 (2.66 GHz) No Turbo Boost 17