HP DL360 The Intel processor roadmap for industry-standard servers technology - Page 19
Dynamic Power Management, More operating power states and lower idle processor power states
 |
UPC - 613326948835
View all HP DL360 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 19 highlights
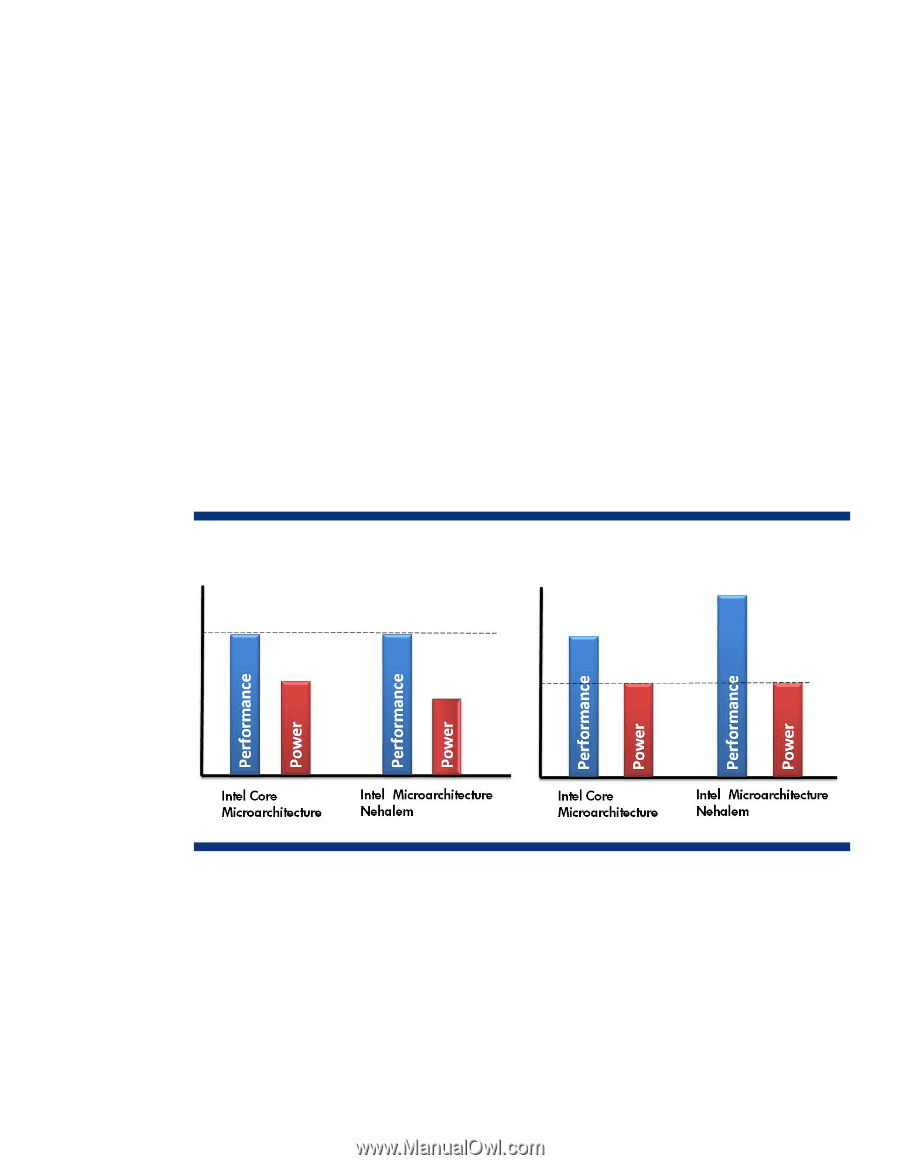
heat savings realized by disabling processor cores allows the remaining cores to run at a higher frequency than their rated speed. In specific application environments, this may actually increase overall system performance. • Addressing licensing issues. Some software is licensed on a per-core basis. Disabling cores allows an administrator to match the number of active cores on a server with licensing requirements. However, some software that is licensed on a per-core basis may not recognize the disabling of cores unless the core is disabled through the BIOS during POST. Dynamic Power Management Dynamic Power Management works hand-in-hand with Turbo Boost to automatically optimize the performance and power use of the processor, chipset, and memory based on business requirements. Dynamic Power Management provides the following key improvements: • The ability to manage power for the processor, chipset, and memory • More operating power states and lower idle processor power states • Reduced overhead when transitioning states These Dynamic Power Management advances allow a processor based on the Intel Microarchitecture Nehalem to provide greater performance while using the same amount of power as a processor based on the previous generation Intel Core microarchitecture (Figure 13). Conversely, a Nehalem processor can achieve performance equivalent to a previous generation processor and use less power achieving it. Figure 13. Dynamic Power Management Lower power consumption with the same performance Higher performance using the same power 19