Netgear DM111Pv2 DM111Pv2 User Manual - Page 30
Running Diagnostic Utilities and Rebooting the Modem Router, More Information - problem
 |
View all Netgear DM111Pv2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
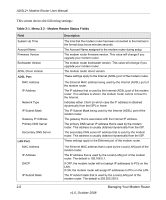
ADSL2+ Modem Router User Manual The upper table indicates how the modem router has detected the ADSL parameters are configured, except for the "Line Up Time", which indicates the time elapsed since the last reset or power cycle. The lower table provides information about the quality of upstream and downstream data. These statistics will be of interest to your technical support representative if you are having problems obtaining or maintaining a connection. Table 2-1. Router Statistics Fields Field Description Line Rate Average data rates. Attainable Line The maximum attainable line rates. Typically, the downstream speed is faster than the Rate upstream speed. Noise Margin This is the signal-to-noise ratio and is a measure of the quality of the signal on the line. The higher the margin, the better the quality. Line Attenuation The line attenuation will increase the further you are physically located from your ISP's facilities. Output Power Indicates the strength of the upstream and downstream signals. Clicking the More Information link will provide more details about the quality of the traffic sent and received, which also may be of interest to your technical support representative if you are having problems obtaining or maintaining a connection. Running Diagnostic Utilities and Rebooting the Modem Router The modem router has a diagnostics feature. You can use the diagnostics menu to perform the following functions from the modem router: • Perform a diagnostic test to check that the unit is working properly. • Display the Routing Table to identify what other modem routers the modem router is communicating with. • Reboot the modem router to enable new network configurations to take effect or to clear problems with the modem router's network connection. 2-8 Managing Your Modem Router v1.0, October 2008