ZyXEL P-2812HNU-F3 User Guide - Page 238
Voice Coding, PSTN Call Setup Signaling, MWI Message Waiting Indication
 |
View all ZyXEL P-2812HNU-F3 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 238 highlights
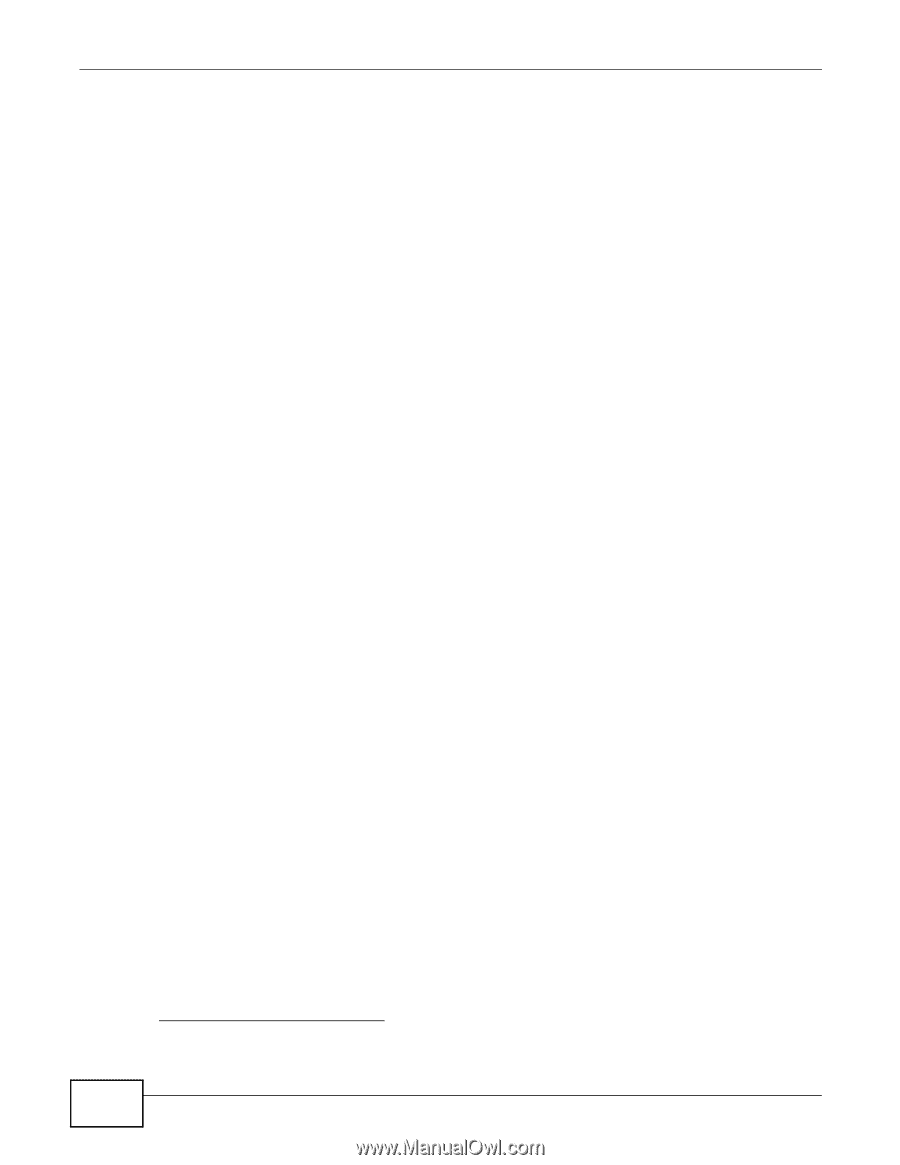
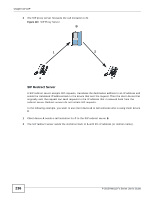
Chapter 16 VoIP 1 A sends a SIP INVITE request to B. This message is an invitation for B to participate in a SIP telephone call. 2 B sends a response indicating that the telephone is ringing. 3 B sends an OK response after the call is answered. 4 A then sends an ACK message to acknowledge that B has answered the call. 5 Now A and B exchange voice media (talk). 6 After talking, A hangs up and sends a BYE request. 7 B replies with an OK response confirming receipt of the BYE request and the call is terminated. Voice Coding A codec (coder/decoder) codes analog voice signals into digital signals and decodes the digital signals back into analog voice signals. The Device supports the following codecs. • G.711 is a Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) waveform codec. PCM measures analog signal amplitudes at regular time intervals and converts them into digital samples. G.711 provides very good sound quality but requires 64 kbps of bandwidth. • G.726 is an Adaptive Differential PCM (ADPCM) waveform codec that uses a lower bitrate than standard PCM conversion. ADPCM converts analog audio into digital signals based on the difference between each audio sample and a prediction based on previous samples. The more similar the audio sample is to the prediction, the less space needed to describe it. G.726 operates at 16, 24, 32 or 40 kbps. • G.729 is an Analysis-by-Synthesis (AbS) hybrid waveform codec that uses a filter based on information about how the human vocal tract produces sounds. G.729 provides good sound quality and reduces the required bandwidth to 8 kbps. PSTN Call Setup Signaling Dual-Tone MultiFrequency (DTMF) signaling uses pairs of frequencies (one lower frequency and one higher frequency) to set up calls. It is also known as Touch Tone®. Each of the keys on a DTMF telephone corresponds to a different pair of frequencies. Pulse dialing sends a series of clicks to the local phone office in order to dial numbers.3 MWI (Message Waiting Indication) Enable Message Waiting Indication (MWI) enables your phone to give you a message-waiting (beeping) dial tone when you have a voice message(s). Your VoIP service provider must have a messaging system that sends message waiting status SIP packets as defined in RFC 3842. 16.10.3 Quality of Service (QoS) Quality of Service (QoS) refers to both a network's ability to deliver data with minimum delay, and the networking methods used to provide bandwidth for real-time multimedia applications. 3. The Device does not support pulse dialing at the time of writing. 238 P-2812HNU(L)-Fx Series User's Guide