Acer Aspire 6600 User Guide - Page 11
Using Your Floppy Drive - download
 |
View all Acer Aspire 6600 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 11 highlights
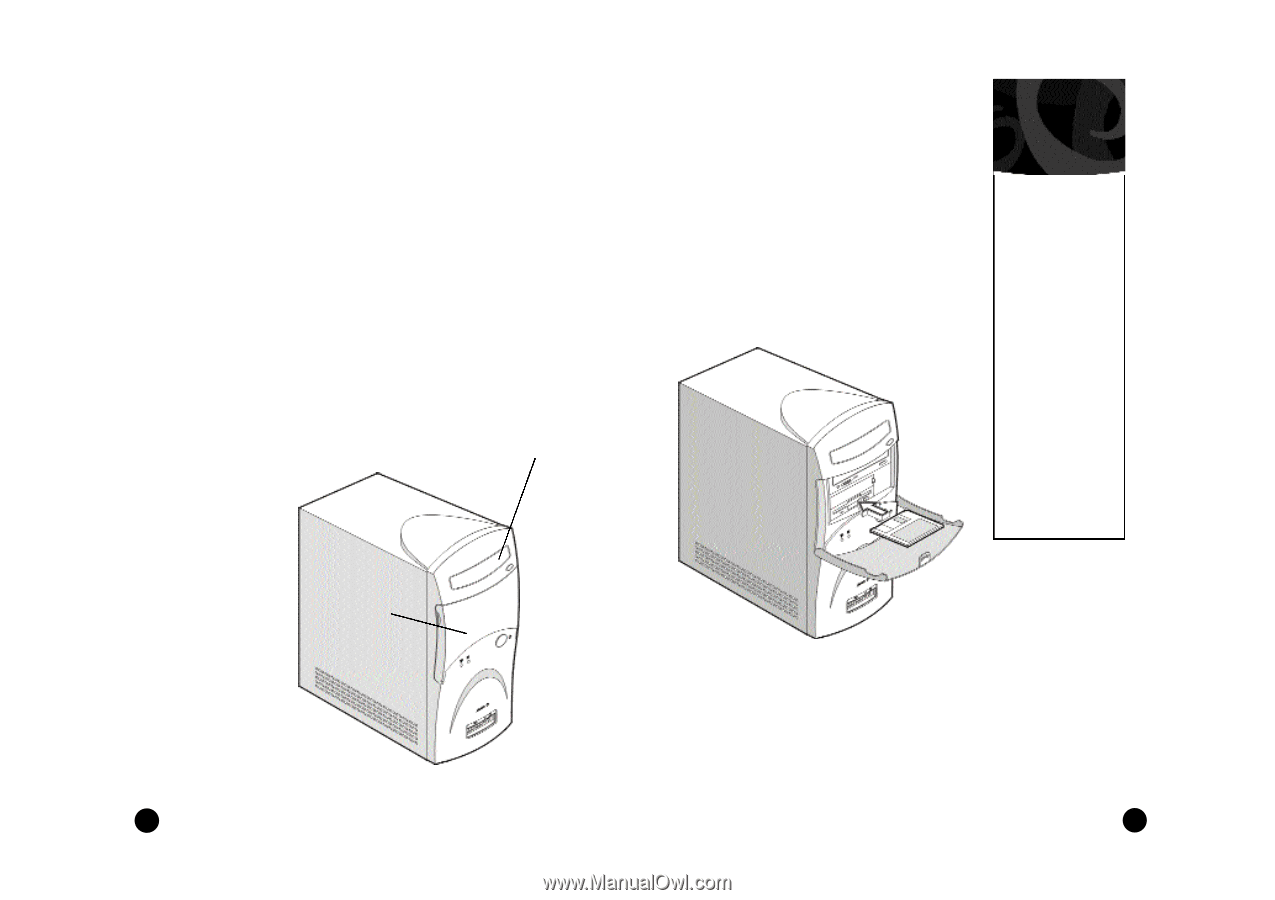
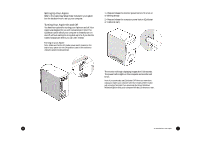
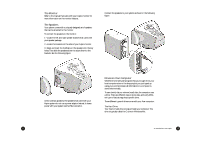
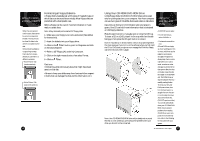
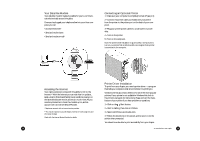
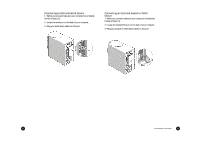
The Floppy Drive This drive uses removable 3.5-inch floppy disks and is called the A: drive. The CD-ROM Drive The CD ROM drive uses CDs (Compact Discs) instead of floppy disks, and it is Read Only Memory, which means that the computer can read data from the disc, but cannot write anything new on it. It is typically called the D: drive. On some computers, the CD-ROM may be another drive letter. Please refer to My Computer for the current drive letter assignment on your Windows Me desktop. The DVD-ROM Drive The DVD-ROM (Digital Versatile Disc or Digital Video Disc Read Only Memory) is a new type of CD-ROM. It can hold capacities ranging from 4.7 GB to a maximum if 17 GB, and can support access rates from 600 Kilobytes per second to 1.2 Megabytes per second. It is backward-compatible with CDROMs which means that DVD players can play not only DVDROMs, but old CD-ROMs, CD-I disks, video CDs, and CD-R disks as well. DVD uses MPEG-2 to compress video data. CD-ROM/ DVD-ROM Drive Note: All of the information you save on your hard drive takes up space, so you will want to clean it up periodically to maintain the best performance. Refer to My Aspire Guide for more information on scanning and analyzing the information on your hard drive. Why Disks? (Or Discs, For that Matter...) Using Your Floppy Drive Floppy disks are used for putting data into your computer or for taking it out. 1 • Insert the floppy disk into the drive, as shown. (The metal circle on the disk's underside should be facing down.) 2 • Push it in gently until it pops into place. 3 • Remove the floppy disk by pressing the eject button. The advantage of a f loppy disk or CD is that it makes data portable. Practically all newly purchased software comes in one of these two formats. Data is often exchanged between computers on floppy disks. Be aware that there is an inherent danger of virus infection in casual swapping or sharing of floppy disks with your friends and associates. Files, applications or programs downloaded from the Internet also carry possible danger. Refer to page 30 for more information. Floppy Drive and Hard Drive 14 An Introduction to Your Aspire 15