Belkin F5D7000 User Manual - Page 13
e Channel, f Client IP Address, g Network Connection Type, h Radio State, i Signal Strength, j Link - manual
 |
View all Belkin F5D7000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 13 highlights
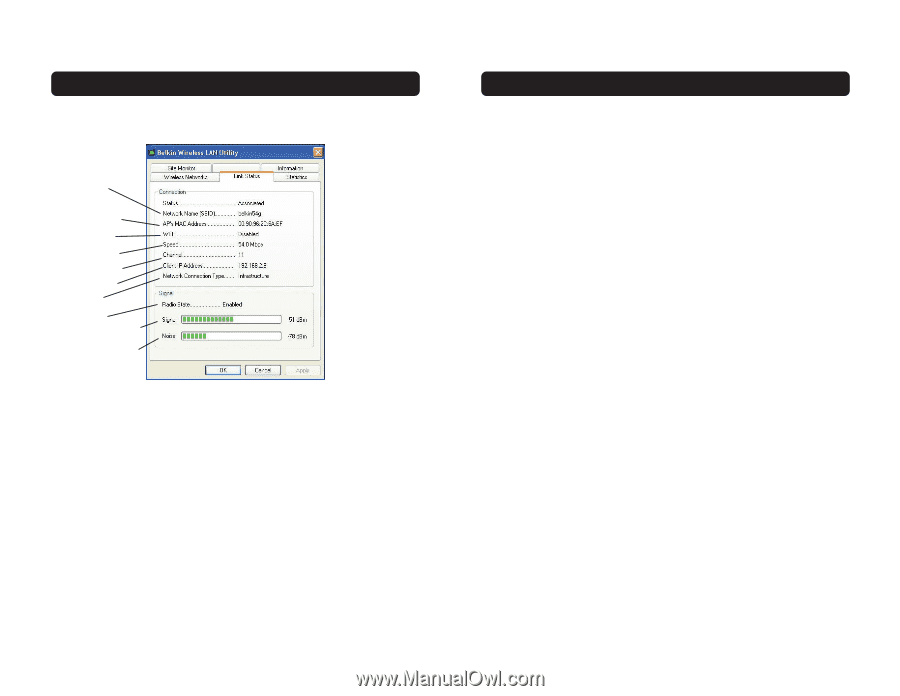
USING THE BELKIN WIRELESS LAN UTILITY The Link Status Tab (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (a) SSID The SSID is the wireless network name. This field shows the current SSID with which the Card is associated. The Card will automatically look for any wireless network in the area. To connect to a specific wireless network, you can manually select the SSID of the known wireless network in the Wireless Networks tab. (b) MAC Address Shows the MAC address of the wireless network that you are connected to. (c) WEP Shows whether the network you are associated with has WEP encryption enabled or disabled. (d) Speed Displays the data rate of the current connection. 22 USING THE BELKIN WIRELESS LAN UTILITY (e) Channel Shows the current channel the Card is operating on. When operating in Infrastructure mode, the channel is set automatically by the access point or wireless router that the Card is connected to. You cannot change the channels in Infrastructure mode. In Ad-Hoc mode, the channel can be set manually. (f) Client IP Address Shows the IP address of the your wireless client. The IP address is obtained automatically by default. You may set the IP address manually through Windows Networking Properties. (g) Network Connection Type Shows the current wireless mode the Card is operating in. There are two operating modes: Infrastructure and Ad-Hoc. Infrastructure is the most common mode to operate in. Infrastructure mode is used when connecting your PC to a wireless access point or to a wireless router. Ad-Hoc mode is used to connect two or more computers together without the use of an access point or wireless router. (h) Radio State Shows whether the IP address of your wireless client is enabled or disabled. The IP address is obtained automatically by default. You may set the IP address manually through Windows Networking Properties. (i) Signal Strength Displays the strength of the wireless signal from 0 to 100%. The closer to 100%, the better the signal strength is. The closer you are to a wireless router or access point, the stronger the signal should be. (j) Link Quality (Noise) Displays the amount of radio interference in the environment. Lower noise ratings are optimal. 23