HP D330 HP Business Desktop BIOS - Page 8
Computer Attacks - bios
 |
View all HP D330 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
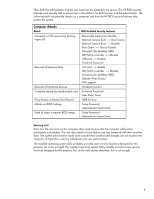
Thus, both the administrator and the user must trust the platform to be secure. The HP BIOS security features work equally well to assure trust in the platform for both the user and the administrator. The following table lists possible attacks on a computer and how the HP BIOS security features help protect the system. Computer Attacks Attack BIOS Enabled Security Features Subversion of OS security by booting rogue OS. Removable media boot disable. Network Service Boot -> Boot Source Network Service Boot -> Disable Boot Order -> Device Disable DriveLock (for MultiBay HDD) IDE/SATA controller -> Disable USB port -> Disable Power-on Password Removal of Sensitive Data I/O port -> disable IDE/SATA controller -> Disable DriveLock (for MultiBay HDD) Diskette Write Protect TPM support Removal of hardware devices Hoodlock Control Computer startup by unauthorized users Power-on Password User Smart Card Virus threats on Master Boot Record MBR Security Attacks on BIOS Settings Setup Password Administrator Smart Card Flash of rogue computer BIOS image Setup Password Administrator Smart Card Securing trust Each time the user turns on the computer, they need to know that the computer will function predictably and reliably. The user also needs to know that no one has tampered with their sensitive data. The system administrator wants to be assured that unauthorized changes are not made to the computer configuration, even by individuals with user authorization. The installed operating system (OS) probably provides some security functions designed for this purpose, but is this enough? The installed operating system (OS) probably provides some security functions designed for this purpose, but, as the next section describes, this is not enough. 8