Kyocera ECOSYS FS-4100DN FS-2100DN/4100DN/4200DN/4300DN Operation Guide - Page 307
SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, SD/SDHC Memory Card
 |
View all Kyocera ECOSYS FS-4100DN manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 307 highlights
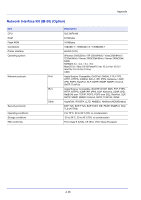
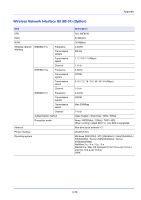
Glossary printing and two-byte languages (e.g. Japanese) in 1990. In 1996, Level 3 was released as an update for the Internet access and PDF format as well as gradual improvements in implementation technologies. PPM (Prints Per Minute) This indicates the number of A4 size printouts made in one minute. Printer driver The software to enable you to print data created on any application software. The printer driver for the machine is contained in the Product Library disc enclosed in the package. Install the printer driver on the computer connected to the machine. RA (Stateless) The IPv6 router communicates (transmits) information such as the global address prefix using ICMPv6. This information is the Router Advertisement (RA). ICMPv6 stands for Internet Control Message Protocol, and is an IPv6 standard defined in the RFC 2463 "Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMPv6) for the Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) Specification". SD/SDHC Memory Card An SD Memory Card is a removable storage media. It is nonvolatile semiconductor memory where the data remains even when the power supply is cut. The maximum memory capacity is 2 GB. SDHC memory cards are a higher specification of SD memory cards. These memory cards have bigger capacities than SD memory cards and have a guaranteed minimum transfer speed. As the file system was changed to FAT32, up to a maximum of 32 GB is supported. Sleep mode This mode is provided to save power. It is activated when the machine is not used for a preset period of time. In this mode, power is reduced to the minimum. The default setting can be changed. SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) A protocol for E-mail transmission over the Internet or an intranet. It is used for transferring mail between mail servers as well as for sending mail from clients to their servers. SSD (Solid State Drive) An SSD is a media for data storage using flash memory. Whereas HDD generally use magnetic discs as the storage media, SDD are a storage media which use semiconductors. Compared with HDD, on which a head reads from the magnetic disk, the merits of SSD are that they can read data at higher speeds, they are resistant to vibrations, and they do not require motors, which mean that they consume less electricity and there is no drive noise. Status page This lists machine conditions, such as the machine's memory, the total number of prints and paper source settings. You can print the status page from the operation panel. Subnet Mask The subnet mask is a way of augmenting the network address section of an IP address. A subnet mask represents all network address sections as 1 and all host address sections as 0. The number of bits in the prefix indicates the length of the network address. The term "prefix" refers to something added to the beginning and, in this context, indicates the first section of the IP address. When an IP address is written, the length of the network address can indicated by the prefix length after a forward slash (/). For example, "24" in the address "133.210.2.0/24". In this way, "133.210.2.0/24" denotes the IP address "133.210.2.0" with a 24-bit prefix (network section). This new network address section (originally part of the host address) made possible by the subnet mask is referred to as the subnet address. When you enter the subnet mask, be sure to set the DHCP setting to Off. Glossary-3