Lexmark X782e IPDS Emulation User’s Guide - Page 113
D. Bar Code Support: 2-D Bar Codes
 |
View all Lexmark X782e manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 113 highlights
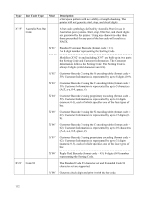
D. Bar Code Support: 2-D Bar Codes Two-dimensional (2-D) bar codes (sometimes called matrix symbologies) allow large amounts of data to be encoded in a small area. The information is represented in a two-dimensional matrix. The printer supports four 2-D bar code symbologies as shown in the table below. Column Labels: Type = Value for Bar Code Type (Bar Code Symbol Descriptor Byte 12; Bar Code Data Descriptor Byte 16) Mod = Modifier Value (Bar Code Symbol Descriptor Byte 13; Bar code Data Descriptor Byte 17) Type Bar Code Type Mod Description 1C Data Matrix 00 Print a Data Matrix bar code symbol using error checking and correcting algorithm 200 as defined in the AIM International Symbology Specification - Data Matrix. 1D MaxiCode 00 Print a MaxiCode bar code symbol as defined in the AIM International Symbology Specification - MaxiCode. 1E PDF417 PDF417 bar code as defined in the AIM International Symbology Specification - PDF417. 00 Print a full PDF417 bar code symbol. 01 Print a truncated PDF417 bar code symbol. The right row indicator is not printed and the stop pattern is printed in a single module width bar. For use in a relatively clean environment where risk of damage to the bar code is minimal. 20 QR Code 02 Print a Model 2 QR Bar Code symbol as defined in AIM International Symbology Specification - QR Code. The printer supports several additional parameters defined for printing bar codes in the IPDS data stream. These parameters are described in the following sections. Additional information on these parameters may be found in the "Bar Code Object Content Architecture (BCOCA) Reference" (publication S5443766-05). 113