Motorola SB6120 User Guide - Page 20
Configuring TCP/IP in Windows 2000 - cannot connect
 |
UPC - 612572169292
View all Motorola SB6120 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 20 highlights
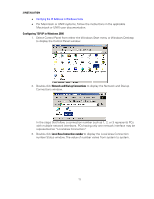
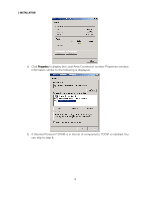
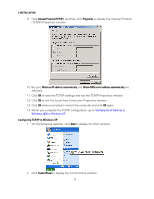
2 INSTALLATION • Verifying the IP Address in Windows Vista • For Macintosh or UNIX systems, follow the instructions in the applicable Macintosh or UNIX user documentation. Configuring TCP/IP in Windows 2000 1. Select Control Panel from either the Windows Start menu or Windows Desktop to display the Control Panel window. 2. Double-click Network and Dial-up Connections to display the Network and Dial-up Connections window. In the steps that follow, a connection number such as 1, 2, or 3 represents PCs with multiple network interfaces. PCs having only one network interface may be represented as "Local Area Connection." 3. Double-click Local Area Connection number to display the Local Area Connection number Status window. The value of number varies from system to system. 13