Netgear N300 User Manual - Page 7
When to Use Your Extender, How the Extender Works
 |
View all Netgear N300 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 7 highlights
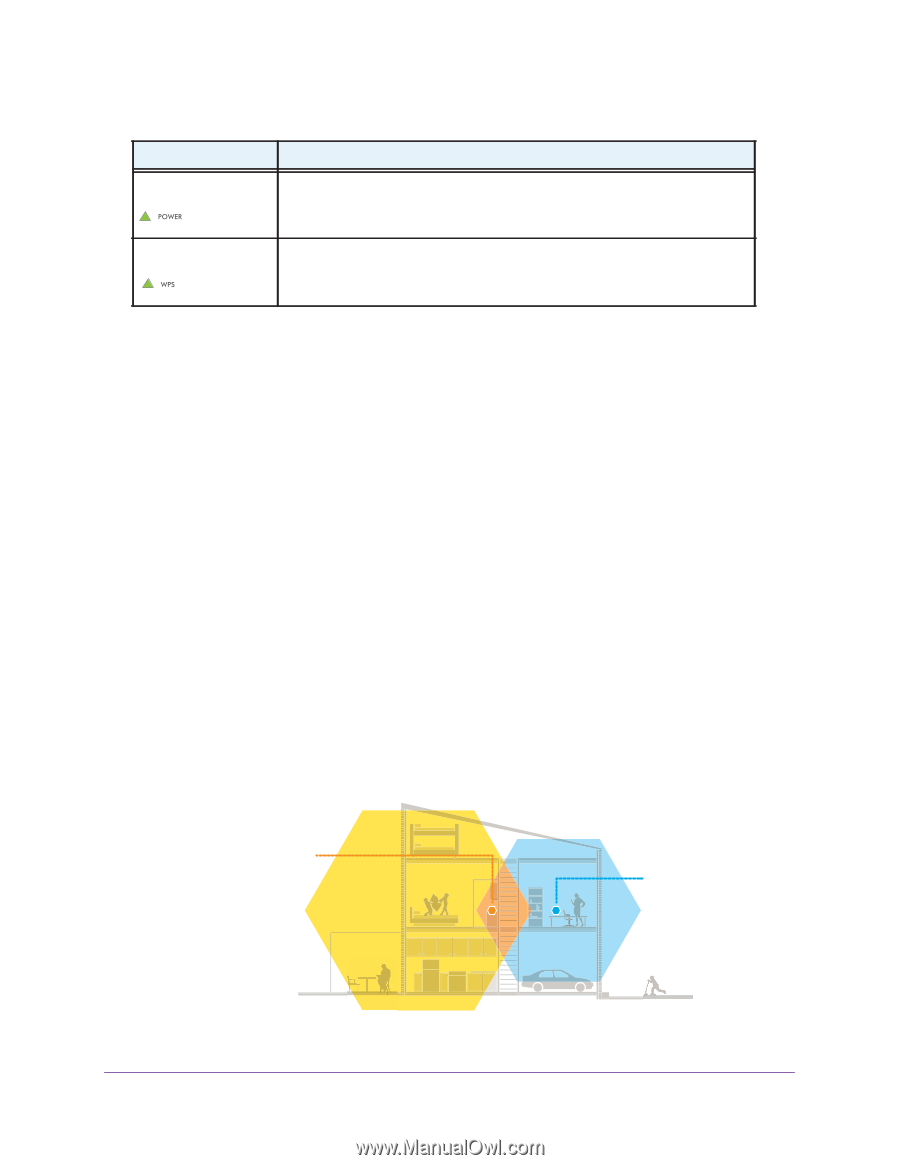
N300 WiF Range Extender Table 1. Front panel LEDs (continued) LED Power WPS Description • Solid amber. The extender is booting. • Solid green. The extender is powered on. • Off. The extender is powered off. • Solid green. WiFi security is enabled (WPA or WPA2). • Blinking green. A WPS connection is being established. • Off. WiFi security is not enabled. When to Use Your Extender We recommend that you connect through the extender network only when the WiFi device is in a "dead zone" where connection from the existing network is poor or nonexistent. Data traffic routed through the extender is inherently slower than traffic routed directly from the network. How the Extender Works The extender works like a bridge between a WiFi router (or a WiFi access point) and a WiFi device outside the range of the WiFi router. The extender performs two main jobs: • The extender connects to a working WiFi network. When the extender connects over WiFi to an existing network, it functions as a network client, similar to how a WiFi device connects to a network. • The extender acts as an access point for WiFi devices. The extender broadcasts its own WiFi network that WiFi devices can join. In its role as an access point, the extender performs tasks that WiFi routers do, such as broadcasting its network name (SSID). The extender must do each of these jobs so that both ends of the bridge are in place. WiFi Range Extender Boosts the range of your existing WiFi and creates a stronger signal in hard-to-reach areas. Figure 2. Range extender in a home Overview 7 Existing WiFi Sometimes your router does not provide the WiFi coverage that you need.