Stihl MS 193 C-E Product Instruction Manual - Page 16
See the on Low Kickback Saw - test
 |
View all Stihl MS 193 C-E manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 16 highlights
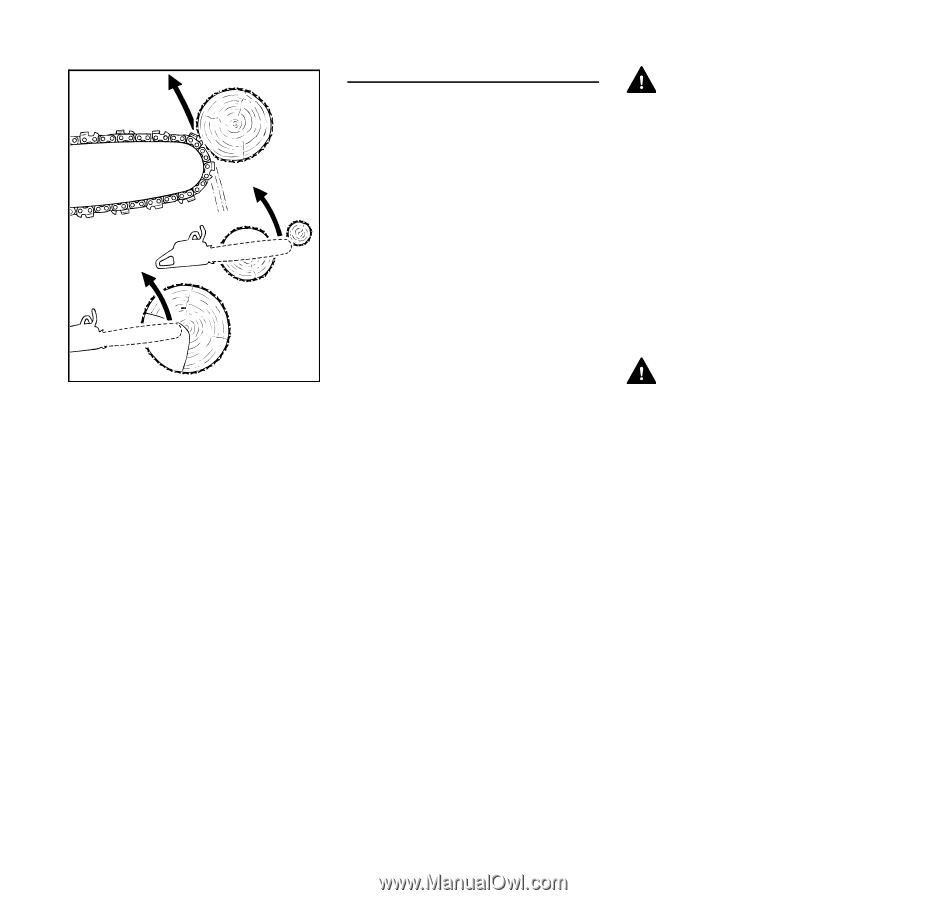
English Kickback may occur, for example, when the saw chain near the upper quadrant of the bar nose contacts the wood or is pinched during limbing or when it is incorrectly used to begin a plunge or boring cut. The greater the force of the kickback reaction, the more difficult it becomes for the operator to control the chain saw. Many factors influence the occurrence and force of the kickback reaction. These include saw chain speed, the speed at which the bar and saw chain contact the object, the angle of contact, the condition of the saw chain and other factors. The type of bar and saw chain you use is an important factor in the occurrence and force of the kickback reaction. Some STIHL bar and saw chain types are designed to reduce kickback forces. STIHL recommends the use of reduced kickback bars and low kickback chains. 001BA035 KN Chain Saw Kickback Standard The following standard apply with respect to kickback: - § 5.11 of ANSI/OPEI B175.1-2012 This standard, in the following referred to as "the chain saw kickback standard" sets certain performance and design criteria related to chain saw kickback. To comply with the chain saw kickback standard: a) Chain saws with a displacement of less than 3.8 cubic inches (62 cm³) - must, in their original condition, meet a 45° computer derived kickback angle when equipped with certain cutting attachments, - and must be equipped with at least two devices to reduce the risk of kickback injury, such as a chain brake, low kickback saw chain, reduced kickback bar, etc. b) Chain saws with a displacement of 3.8 cubic inches (62 cm³) and above - must be equipped with at least one device designed to reduce the risk of kickback injury, such as a chain brake, low kickback saw chain, reduced kickback bar, etc. The computer derived angles for chain saws below 3.8 cubic inches (62 cm³) displacement are measured by applying a computer program to test results from a kickback test machine. WARNING The computer derived angles of the chain saw kickback standard may bear no relationship to actual kickback bar rotation angles that may occur in real life cutting situations. In addition, features designed to reduce kickback injuries may lose some of their effectiveness when they are no longer in their original condition, especially if they have been improperly maintained. Compliance with the chain saw kickback standard does not automatically mean that in a real life kickback the bar and saw chain will rotate at most 45°. WARNING In order for chain saws below 3.8 cubic inches (62 cm³) displacement to comply with the computed kickback angle requirements of the chain saw kickback standard use only the following cutting attachments: - bar and saw chain combinations listed as complying in the "Specifications" section of the instruction manual or - other replacement bar and saw chain combinations marked in accordance with the standard for use on the chain saw or - replacement saw chain designated "low kickback saw chain." See the section on "Low Kickback Saw Chain and Reduced Kickback Bars." 14 MS 193 C