ZyXEL NWA1123-NI User Guide - Page 13
Wireless Client, VoIP_SSID, SSID01, Guest_SSID - dual radio
 |
View all ZyXEL NWA1123-NI manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 13 highlights
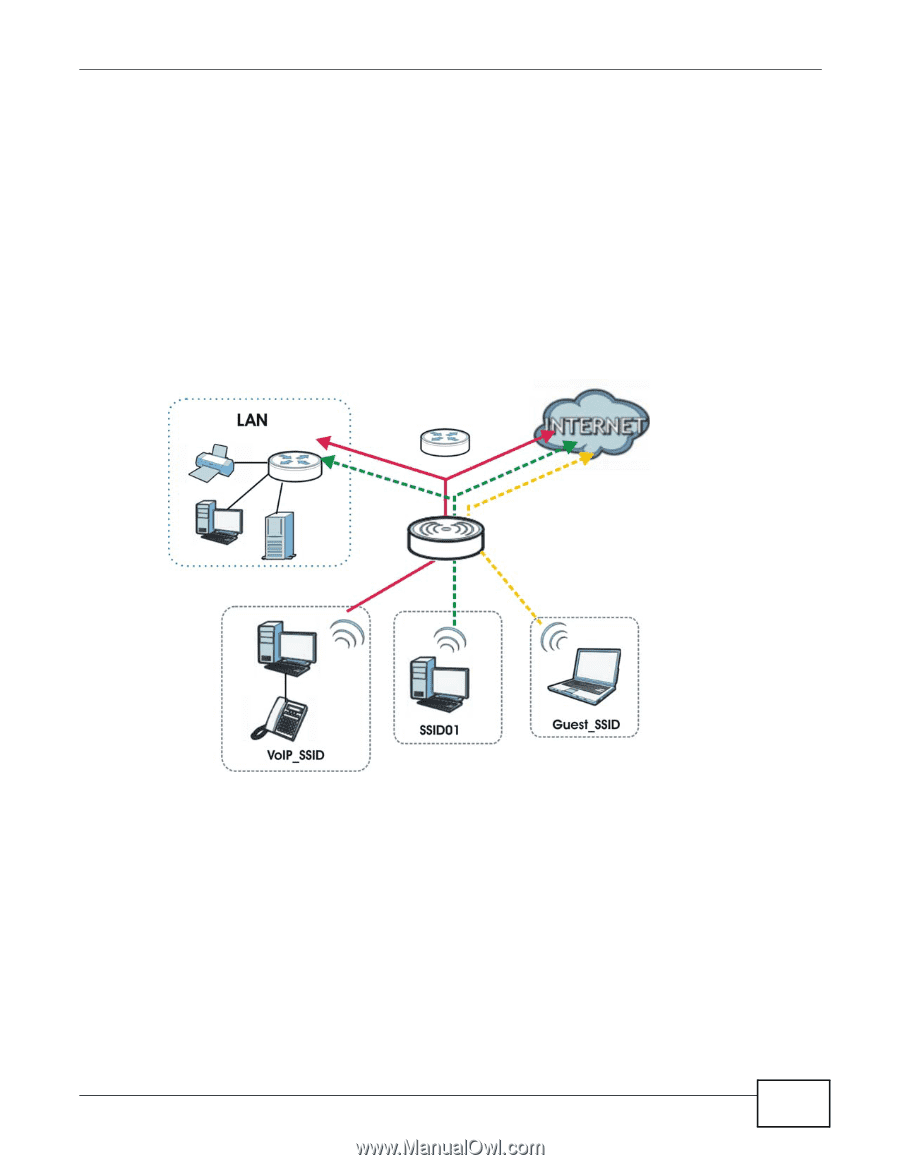
Chapter 1 Introducing the NWA You can assign different wireless and security settings to each SSID profile. This allows you to compartmentalize groups of users, set varying access privileges, and prioritize network traffic to and from certain BSSs. To the wireless clients in the network, each SSID appears to be a different access point. As in any wireless network, clients can associate only with the SSIDs for which they have the correct security settings. For example, you might want to set up a wireless network in your office where Internet telephony (VoIP) users have priority. You also want a regular wireless network for standard users, as well as a 'guest' wireless network for visitors. In the following figure, VoIP_SSID users have QoS priority, SSID01 is the wireless network for standard users, and Guest_SSID is the wireless network for guest users. In this example, the guest user is forbidden access to the wired Land Area Network (LAN) behind the AP and can access only the Internet. Figure 2 Multiple BSSs 1.2.2 Wireless Client The NWA can be used as a wireless client to communicate with an existing network. Note: The NWA1123-NI is a dual-band AP which contains two different types of wireless radios to transmit at 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands separately and simultaneously. If one of the NWA1123-NI wireless radio is set to work in client mode, the other radio will be disabled automatically. NWA1120 Series User's Guide 13