ZyXEL NWA1123-NI User Guide - Page 63
WPA-PSK, Table 11, LABEL, DESCRIPTION, Local MAC Address, Dynamic, CTS to self, RTS-CTS, 11b/g/n
 |
View all ZyXEL NWA1123-NI manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 63 highlights
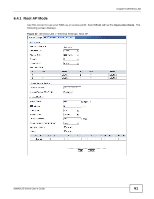
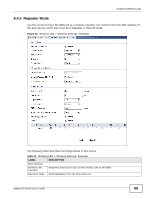
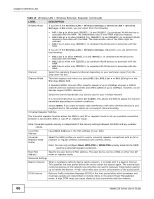
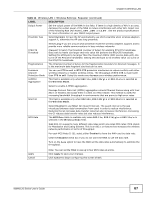
Chapter 6 Wireless LAN Table 11 Wireless LAN > Wireless Settings: Root AP (continued) LABEL DESCRIPTION Universal Repeater Settings The Universal repeater function allows the NWA in root AP or repeater mode to set up a wireless connection between it and another NWA in root AP or repeater mode. Note: Universal repeater security is independent of the security settings between the NWA and any wireless clients. Local MAC Address Local MAC Address is the MAC address of your NWA. Universal Repeater SSID Profile Select the SSID profile you want to use for universal repeater connections. Note: You can only configure None, WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK security mode for the SSID used by a universal repeater connection. Advanced Settings Beacon Interval When a wirelessly network device sends a beacon, it includes with it a beacon interval. This specifies the time period before the device sends the beacon again. The interval tells receiving devices on the network how long they can wait in lowpower mode before waking up to handle the beacon. A high value helps save current consumption of the access point. DTIM Interval Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM) is the time period after which broadcast and multicast packets are transmitted to mobile clients in the Active Power Management mode. A high DTIM value can cause clients to lose connectivity with the network. Output Power Set the output power of the NWA in this field. If there is a high density of APs in an area, decrease the output power of the NWA to reduce interference with other APs. Select one of the following Full (Full Power), 50%, 25%, or 12.5%. See the product specifications for more information on your NWA's output power. Preamble Type Select Dynamic to have the AP automatically use short preamble when wireless adapters support it, otherwise the AP uses long preamble. RTS/CTS Threshold Fragmentation Extension Channel Protection Mode A-MPDU Aggregation Select Long if you are unsure what preamble mode the wireless adapters support, and to provide more reliable communications in busy wireless networks. (Request To Send) The threshold (number of bytes) for enabling RTS/CTS handshake. Data with its frame size larger than this value will perform the RTS/CTS handshake. Setting this attribute to be larger than the maximum MSDU (MAC service data unit) size turns off the RTS/CTS handshake. Setting this attribute to its smallest value (1) turns on the RTS/CTS handshake. The threshold (number of bytes) for the fragmentation boundary for directed messages. It is the maximum data fragment size that can be sent. You can use CTS to self or RTS-CTS protection mechanism to reduce conflicts with other wireless networks or hidden wireless clients. The throughput of RTS-CTS is much lower than CTS to self. Using this mode may decrease your wireless performance. This field is available only when 802.11n, 802.11b/g/n or 802.11a/n is selected as the Wireless Mode. Select to enable A-MPDU aggregation. Short GI Message Protocol Data Unit (MPDU) aggregation collects Ethernet frames along with their 802.11n headers and wraps them in a 802.11n MAC header. This method is useful for increasing bandwidth throughput in environments that are prone to high error rates. This field is available only when 802.11n, 802.11b/g/n or 802.11a/n is selected as the Wireless Mode. Select Enabled to use Short GI (Guard Interval). The guard interval is the gap introduced between data transmission from users in order to reduce interference. Reducing the GI increases data transfer rates but also increases interference. Increasing the GI reduces data transfer rates but also reduces interference. NWA1120 Series User's Guide 63