HP 1606 Fabric Watch Administrator's Guide v6.4.0 (53-1001770-01, June 2010) - Page 61
Fabric, Security, SFP, and Performance Monitoring, In
 |
View all HP 1606 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 61 highlights
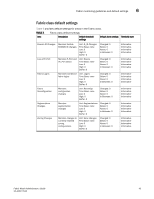
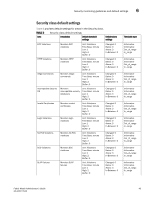
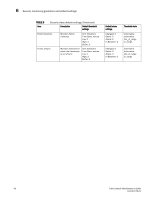
Chapter Fabric, Security, SFP, and Performance Monitoring 6 In this chapter •Fabric monitoring guidelines and default settings 41 •Security monitoring guidelines and default settings 44 •SFP monitoring guidelines and default settings 47 •Performance monitoring guidelines and default settings 49 •Configuration options for thConfig command 51 •Customizing thConfig command settings 52 •Recommended settings for Fabric, SFP, Performance, and Security monitoring 54 Fabric monitoring guidelines and default settings The Fabric class groups areas of potential problems arising between devices, including interswitch link (ISL) details, zoning, and traffic. A Fabric class alarm alerts you to problems or potential problems with interconnectivity. Fabric class areas Table 3 lists Product Name areas in the Fabric class and describes each area. Configure the Fabric class using the thConfig command. TABLE 3 Fabric class areas Area Description Domain ID changes Fabric logins Fabric reconfigure E_Port downs Monitors forced domain ID changes. Forced domain ID changes occur when there is a conflict of domain IDs in a single fabric and the principal switch has to assign another domain ID to a switch. Activates when ports and devices initialize with the fabric. Tracks the number of reconfigurations of the fabric. Fabric reconfiguration occurs when: • Two fabrics with the same domain ID are connected. • Two fabrics are joined. • An E_Port or VE_Port goes offline. • A principal link segments from the fabric. Tracks the number of times that an E_Port or VE_Port goes down. E_Ports and VE_Ports go down each time you remove a cable or an SFP (where there are SFP failures or transient errors). 41