HP 1606 Fabric Watch Administrator's Guide v6.4.0 (53-1001770-01, June 2010) - Page 77
Port Monitoring, In this Port class areas
 |
View all HP 1606 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 77 highlights
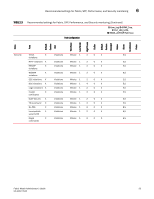
Port Monitoring Chapter 7 In this chapter •Port class areas 57 •Port class guidelines and default settings 59 •Port configuration 68 •portThConfig command procedures 69 •Port fencing 74 •Recommended port configuration settings 78 Port class areas Table 14 lists and describes the Fabric OS v6.4.0 areas in the Port class. Configure the Port class using the portThConfig command. You can find port setting guidelines and specific examples of portThConfig configuration later in this chapter. NOTE Fabric Watch monitors and reports the status of physical and virtual FC ports. Physical GbE ports and ISCSI ports are not monitored and are not included in the Port Class area. TABLE 14 Area Port class areas Indicates CRC ITW C3TX_TO Link loss Signal loss The number of times an invalid cyclic redundancy check error occurs on a port or a frame that computes to an invalid CRC. Invalid CRCs can represent noise on the network. Such frames are recoverable by retransmission. Invalid CRCs can indicate a potential hardware problem. The number of times an invalid transmission word error occurs on a port. A word did not transmit successfully, resulting in encoding errors. Invalid word messages usually indicate a hardware problem. The number of Class 3 discards frames because of timeouts. The number of times a link failure occurs on a port or sends or receives NOS. Both physical and hardware problems can cause link failures. Link failures also frequently occur due to a loss of synchronization or a loss of signal. The number of times that a signal loss occurs in a port. Signal loss indicates that no data is moving through the port. A loss of signal usually indicates a hardware problem. Note: Loss of signal count still displays using the fwConfigure command, but it is no longer supported. 57