HP ProLiant BL660c Electrical signal integrity considerations for HP BladeSyst - Page 10
Target fabrics, Infrastructure architecture, For single-wide switch modules
 |
View all HP ProLiant BL660c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 10 highlights
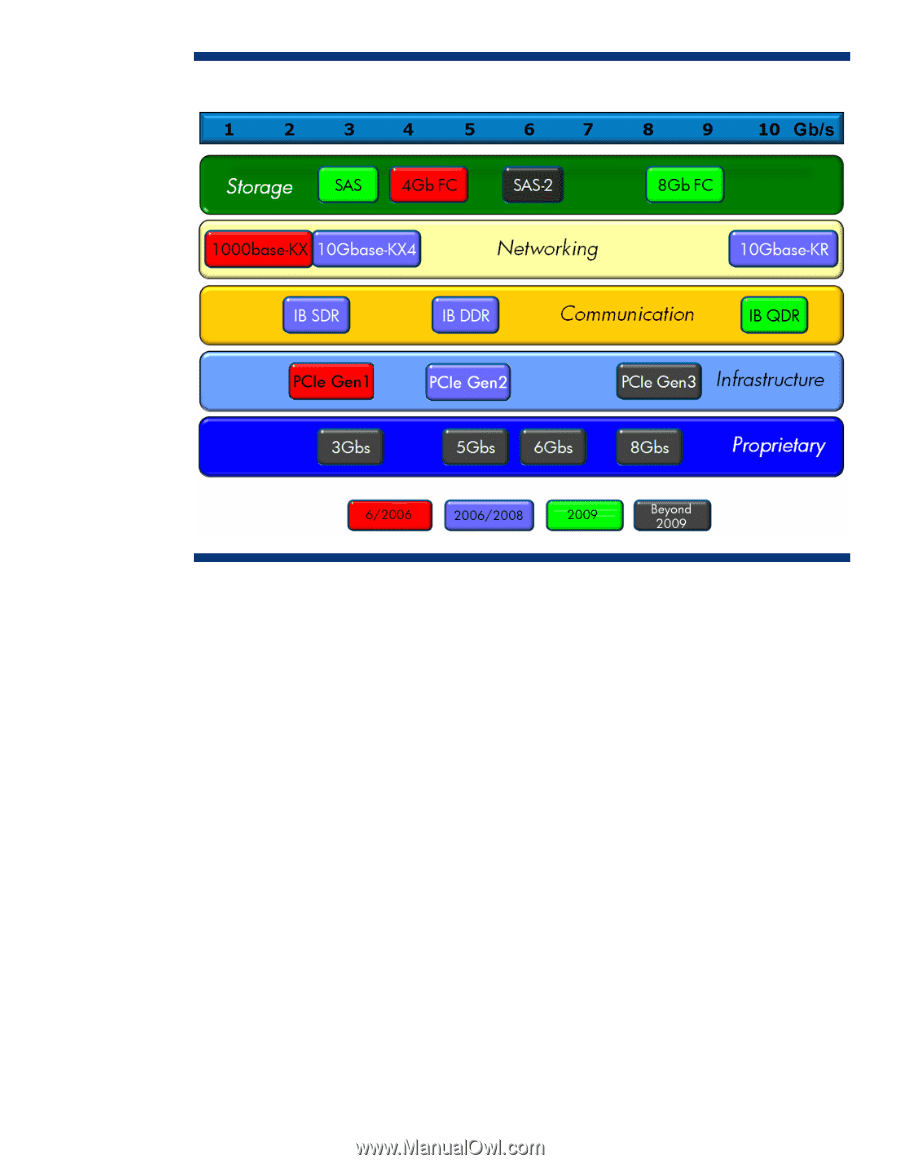
Figure 9. Fabric technology targets Additionally, the design had to incur minimal additional cost for infrastructure to support fabrics yet to be developed, leverage industry standard components, and interoperate with the dozens of companies and multiple divisions involved. Over its lifecycle, the BladeSystem c-Class architecture must support dozens of server blades, more than 50 Mezzanine Cards (MEZZ) and I/O modules, and multiple enclosure designs. Target fabrics The HP BladeSystem provides high-speed interfaces between server blades and switch modules. Server blades may contain components connected to the high-speed interfaces on their motherboards or on mezzanine cards. The main high-speed interface is expected to be used for connecting server blades to switch modules with high-speed differential signals. In various implementations, these channels are used for routing Ethernet, Fibre Channel, or other types of signaling. Infrastructure architecture For single-wide switch modules, each main high-speed interface consists of a group of four pairs of signals, available for use as two lanes (two transmit pairs and two receive pairs) connected to a server blade. Additionally, for single-wide switch modules, there is also an inter-switch link available that allows two adjacent switch modules to communicate for failover, connectivity, and so forth. It consists of eight pairs of signals available for use as four lanes (four transmit pairs and four receive pairs). 10