HP ProLiant BL660c HP BladeSystem c-Class architecture - Page 14
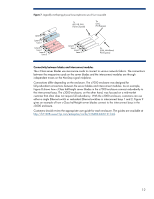
NonStop signal midplane enables modularity
 |
View all HP ProLiant BL660c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 14 highlights
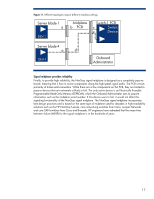
modules. For example, within a given enclosure, all mezzanine cards in the mezzanine 1 connector of the server blades must support the same type of fabric. HP developed the electronic keying mechanism in Onboard Administrator to assist system administrators in recognizing and correcting potential fabric mismatch conditions as they configure each enclosure. Before any server blade or interconnect module is powered up, the Onboard Administrator queries the mezzanine cards and interconnect modules to determine compatibility. If the Onboard Administrator detects a configuration problem, it provides a warning with information about how to correct the problem. NonStop signal midplane enables modularity The architecture of the NonStop signal midplane makes it possible to develop more modular components than those available in previous generations of blade systems. New types of components can be implemented in the blade form factor and connected across the NonStop signal midplane - front-to-back or side-to-side. The front-to-back modularity is supported by installing mezzanine cards in the server blades at the front of the enclosure, and the matching interconnect modules in the rear of the enclosure. For side-to-side modularity, HP has introduced storage blade and local I/O option blades that communicate with an adjacent server blade across the midplane. A storage blade enables a server blade for disk drive capacity expansion, an alternative solution to internal local disk drives or logical unit numbers (LUNs) in a SAN. HP has also developed a tape blade for backup solutions. A PCI Expansion Blade provides PCI card expansion slots so that off-the-shelf PCI-X or PCI-e cards can be attached to an adjacent server blade. These possibilities exist because the NonStop signal midplane can carry either network-semantic traffic or memory-semantic traffic using the same sets of traces. By designing the c-Class enclosure to be a general-purpose system, HP made the architecture adaptive and able to meet the needs of IT applications today and in the future. BladeSystem c-Class architecture provides high bandwidth and compute performance A requirement for any server architecture is that it provides high performance and bandwidth to meet future customer needs. The BladeSystem c-Class enclosure was architected to ensure that it can support upcoming technologies and their demand for bandwidth and power for at least the next 5 to 7 years. It provides this through three design elements: • Blade form factors that enable server-class components • High-bandwidth NonStop signal midplane • Separate power backplane Server-class components To ensure longevity for the c-Class architecture, HP uses a 2-inch wide form factor that accommodates server-class, high-performance components. Choosing a wide form factor allowed HP to design halfheight servers supporting the most common server configurations: two processors, eight full-size DIMM slots with vertical DIMM connectors, two Small Form Factor (SFF) disk drives, and two optional mezzanine cards. When scaled up to the full-height configuration, HP server blades can support approximately twice the resources of a half-height server blade: for example, up to four processors, sixteen full-size DIMM slots, four SFF drives, and three optional mezzanine cards. 14