HP ProLiant BL660c HP BladeSystem c-Class architecture - Page 19
Server blades and processors, Enclosure, Meeting data center configurations - proliant bl460c
 |
View all HP ProLiant BL660c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 19 highlights
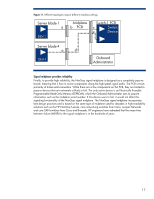
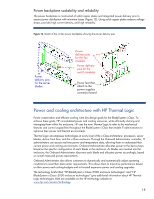
Server blades and processors At the processor level, HP Power Regulator for ProLiant5 is a ROM-based power management feature of HP ProLiant servers. Power Regulator technology takes advantage of the power states available on x86 processors to scale back the power to a processor when it is not needed. Because the c-Class architecture shares power among all server blades in an enclosure, administrators can use Power Regulator technology to balance power loads among the server blades. As processor technology progresses, HP can recommend that customers use lower-power processor and component options when and where possible. The server blade designs use precise ducting throughout the server blade to manage airflow and temperature based on the unique thermal requirements of all the critical components. The airflow is tightly ducted to ensure that no air bypasses the server blade and to obtain the most thermal work from the least amount of air. This concept allows much more flexibility in heat sink design choice. The heat sinks closely match the requirements of the server blade and processor architecture. For example, in the Intel® Xeon® based HP BladeSystem BL460c server blade, HP was able to use a smaller highpower processor heat sink than in rack-mount servers. These heat sinks have vapor chamber bases, thinner fins, and tighter fin pitch than previous designs. The smaller heat sink allows more space for full-size memory modules and hot plug hard drives on the server blades. Most importantly, c-Class server blades incorporate intelligent management processors (Integrated Lights-Out 2, or iLO 2, for ProLiant server blades, or Integrity iLO for Integrity server blades) that provide detailed thermal information for every server blade. This information is forwarded to the Onboard Administrator and is accessible through the Onboard Administrator web interface. Enclosure At the enclosure level, HP Thermal Logic provides a number of advantages: • Power designed to meet data center configurations • High-efficiency voltage conversions • Dynamic Power Saver mode to operate power supplies at high efficiencies • Active Cool Fans that minimize power consumption • Mechanical design features (PARSEC architecture) to optimize airflow Meeting data center configurations Rather than design the power budgets for the c-Class architecture based on the anticipated requirements of server blades, HP designed the c-Class enclosures to conform to typical data center facility power feeds. Thus, the enclosures are sized not only to amortize the cost of server blades across the infrastructure, but also to support the most server blades possible while using the power available today. As IT facilities managers choose to increase the number of power feeds into their facilities, c-Class enclosures can be added that will fit into those typical power feed budgets. Because the enclosures are sized to meets today's power infrastructure, there is no need for a separate power enclosure. High-efficiency voltage conversions Incorporating the power supplies into the enclosure reduced the distance over which power would need to be distributed. This allowed HP to use an industry-standard 12V infrastructure for the c-Class BladeSystem. Using a 12V infrastructure eliminates several power-related components and improves power efficiency on the server blades and infrastructure. 5 For additional information about Power Regulator for ProLiant and which servers support it, see www.hp.com/servers/power-regulator. 19